Myth: Animal agriculture is sustainable.
Sustainability means that cycles are not disturbed and systems are not brought out of balance in the long term.
(1) Metabolism
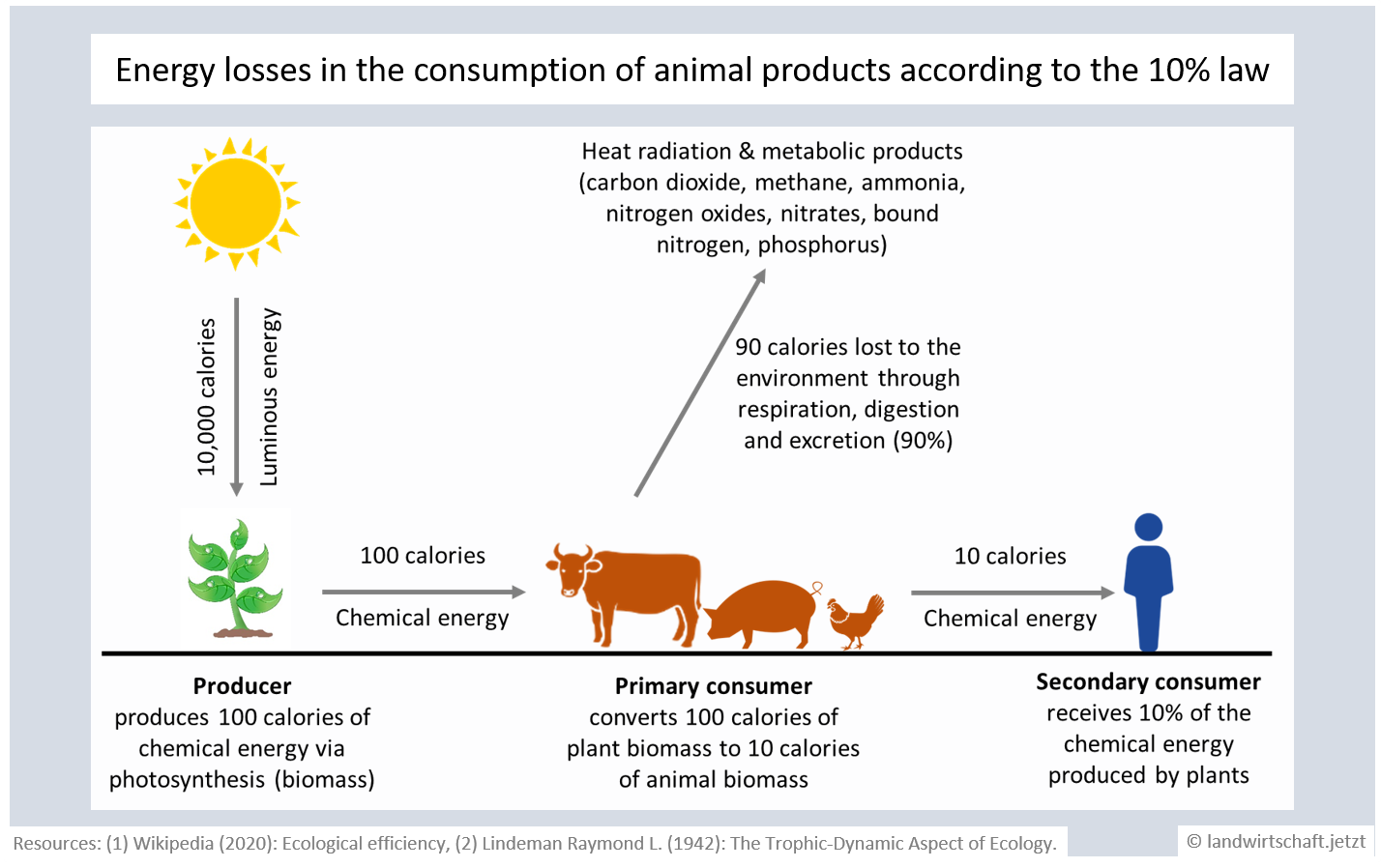
The consumption of animal products is accompanied by considerable losses of usable biomass. On average, 90% of the energy is lost per trophic level through metabolism and respiration ([31],[17]). Due to this energy loss, considerably more resources (agricultural land, water, macro- and micronutrients) have to be expended for the consumption of animal products than for the direct consumption of plants. On the one hand, the energy is lost for human use, and on the other hand, it is released into the environment via harmful metabolic products (greenhouse gases, acidifying and eutrophying substances). The high input of resources and the high output of harmful substances disturb the biogeochemical cycles and bring the material flow balances into imbalance.
(1.1) Resource input
(1.1.1) Land
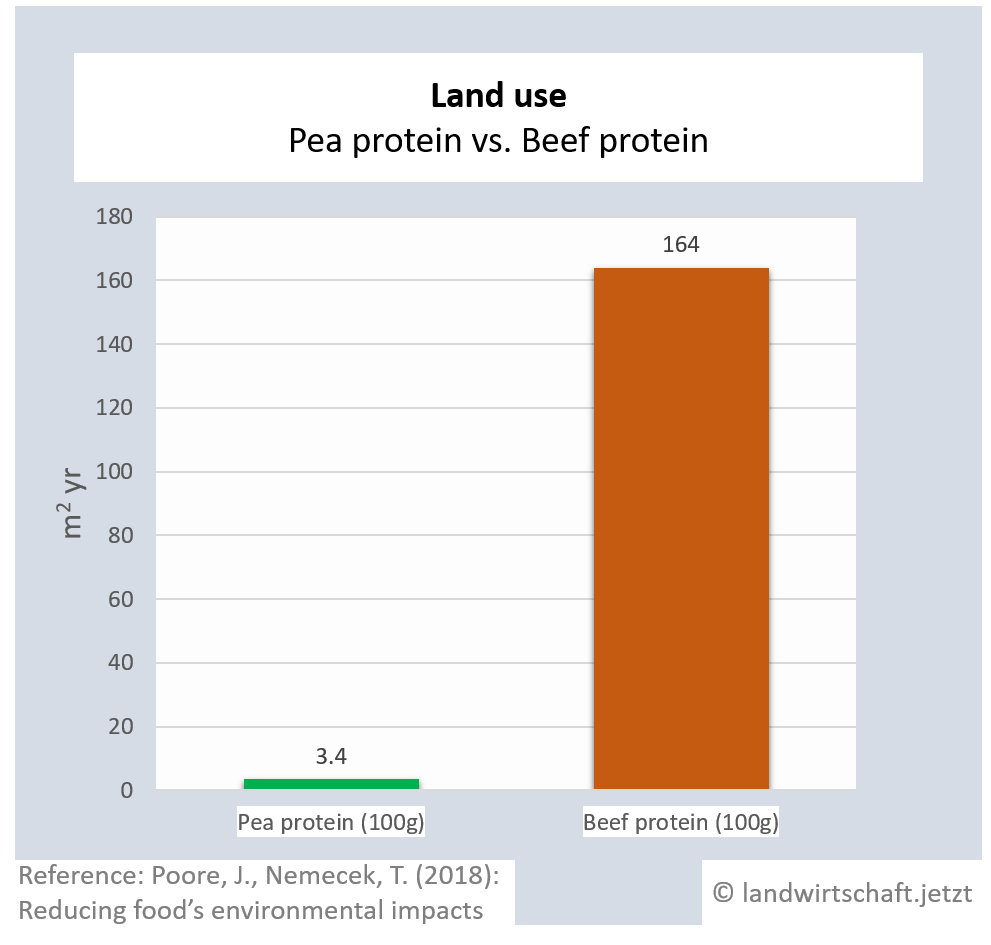
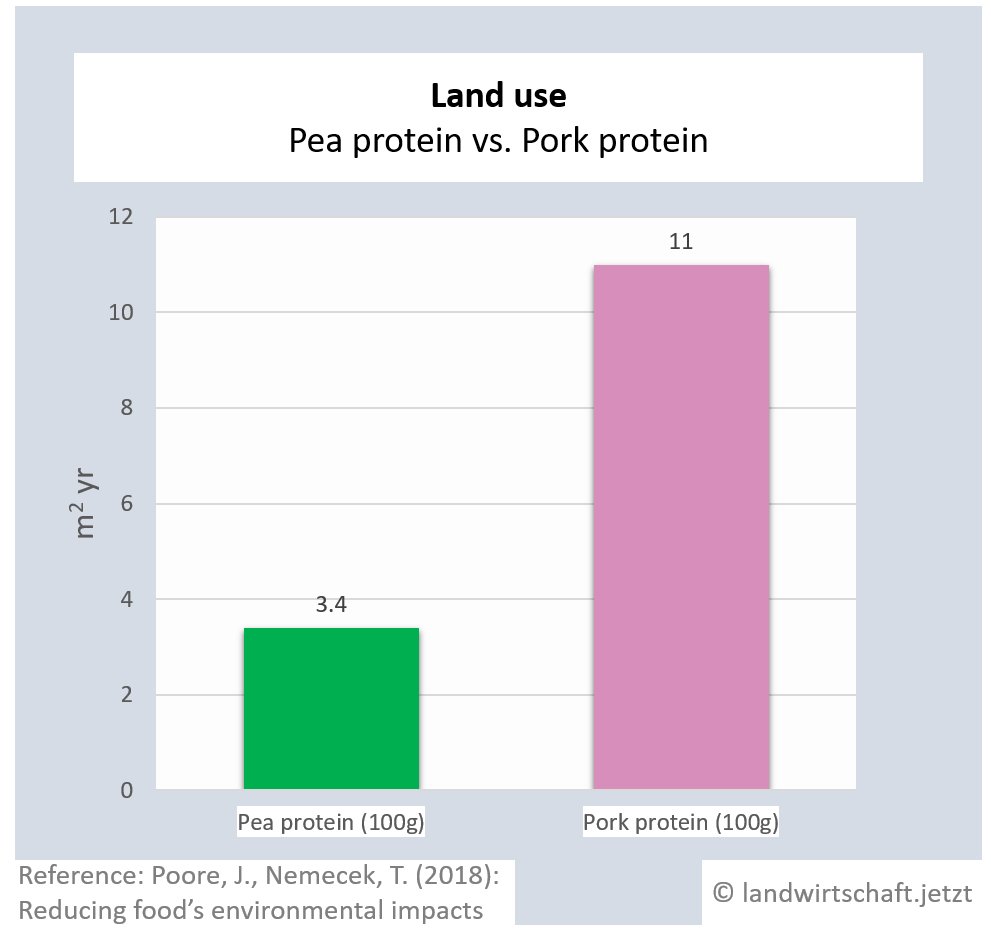
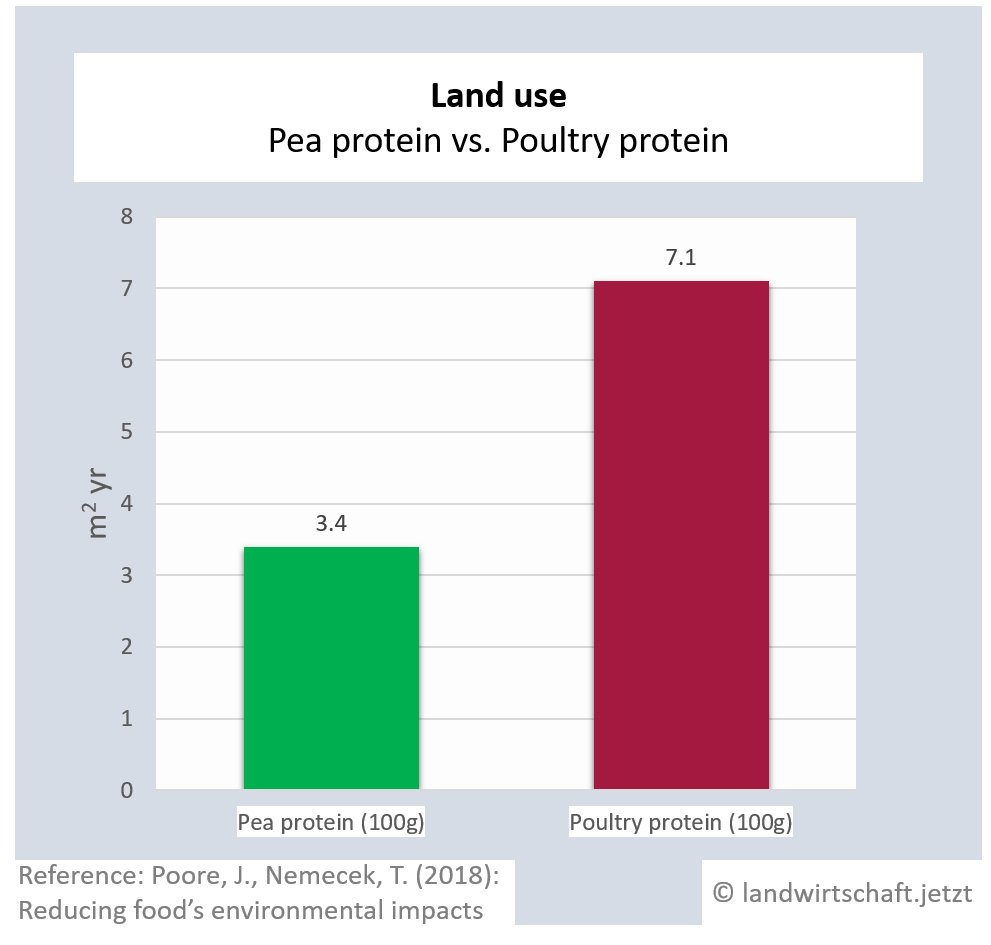
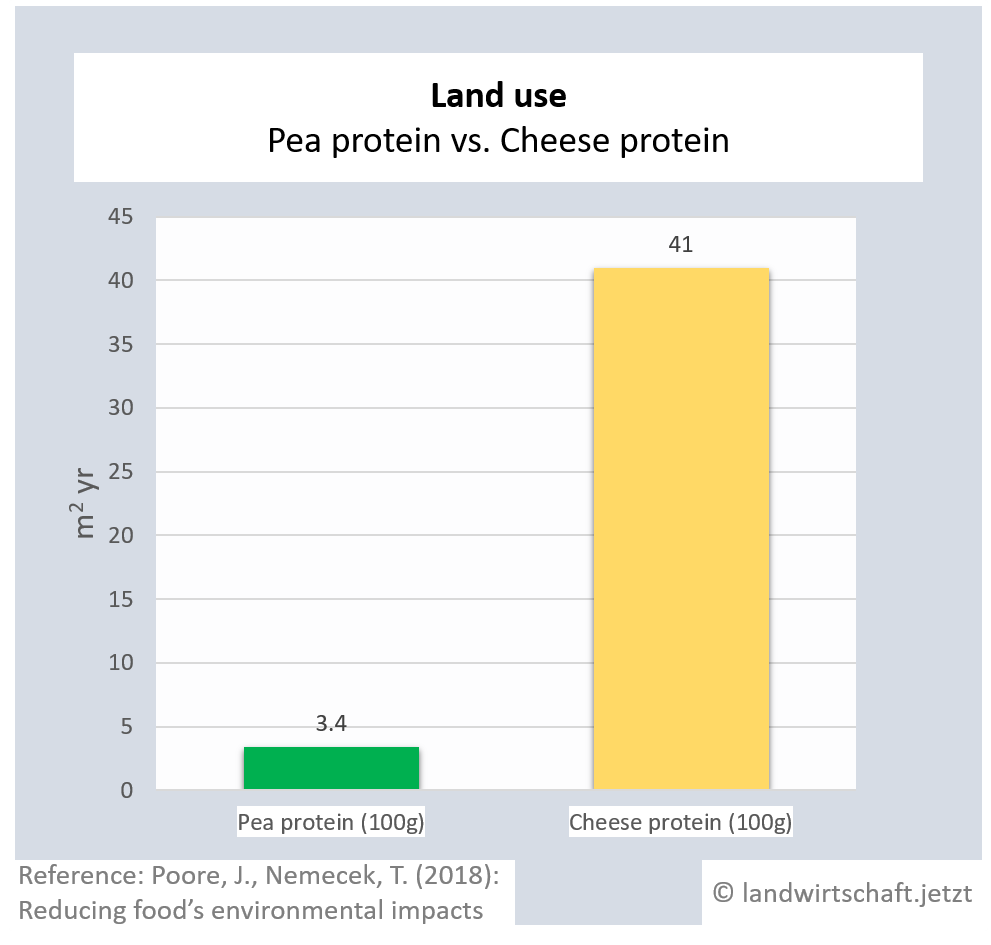
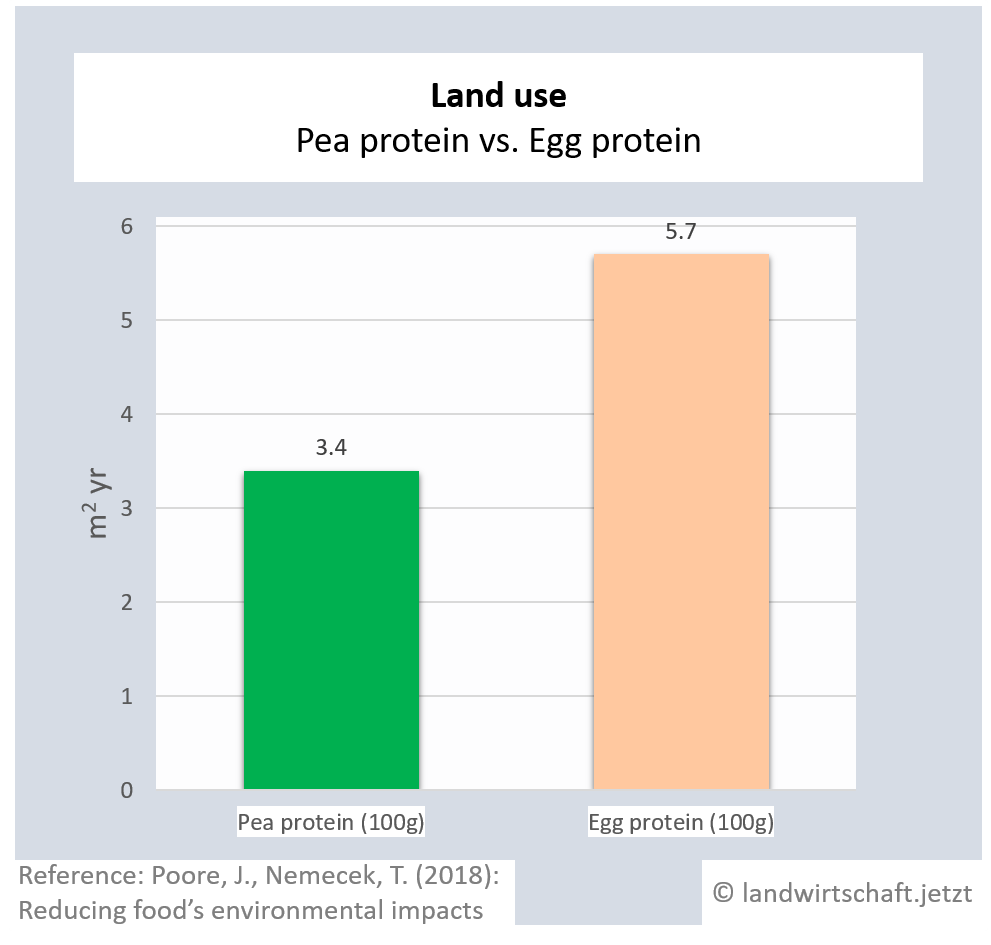
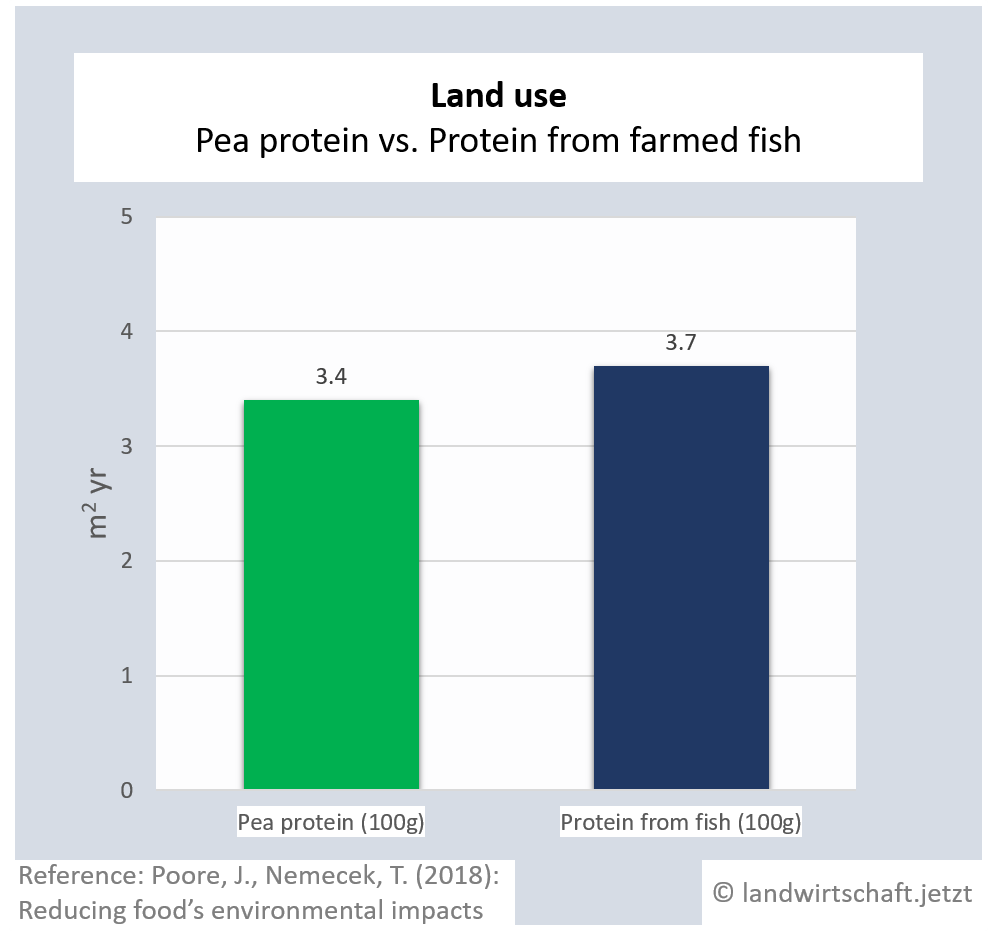
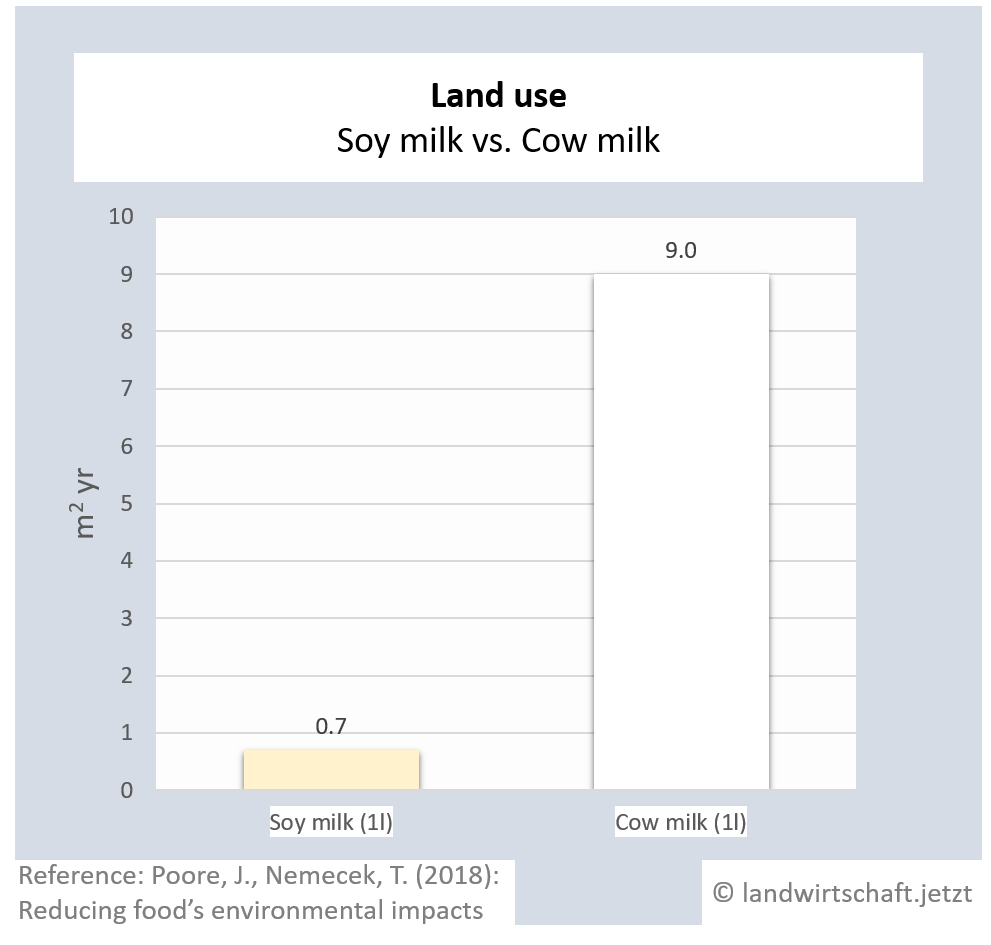
One unit of protein from the production of beef requires 48 times more land than an equivalent unit of protein from the production of peas. For pork, the ratio is 3:1, for poultry 2:1, for cheese 12: 1, for eggs 1.7:1, for fish (farmed) 1:1 and for crustaceans (farmed) 0.6:1. Cow's milk requires more than 13 times as much land as soy milk [6]. This enormously high use of land for animal products is reflected in Bavaria, among other things, by the fact that approx. 60% of agricultural land is used for animal feed ([22], p. 6 ) and yet an additional third of the total protein yield must be imported from overseas for domestic animal agriculture.
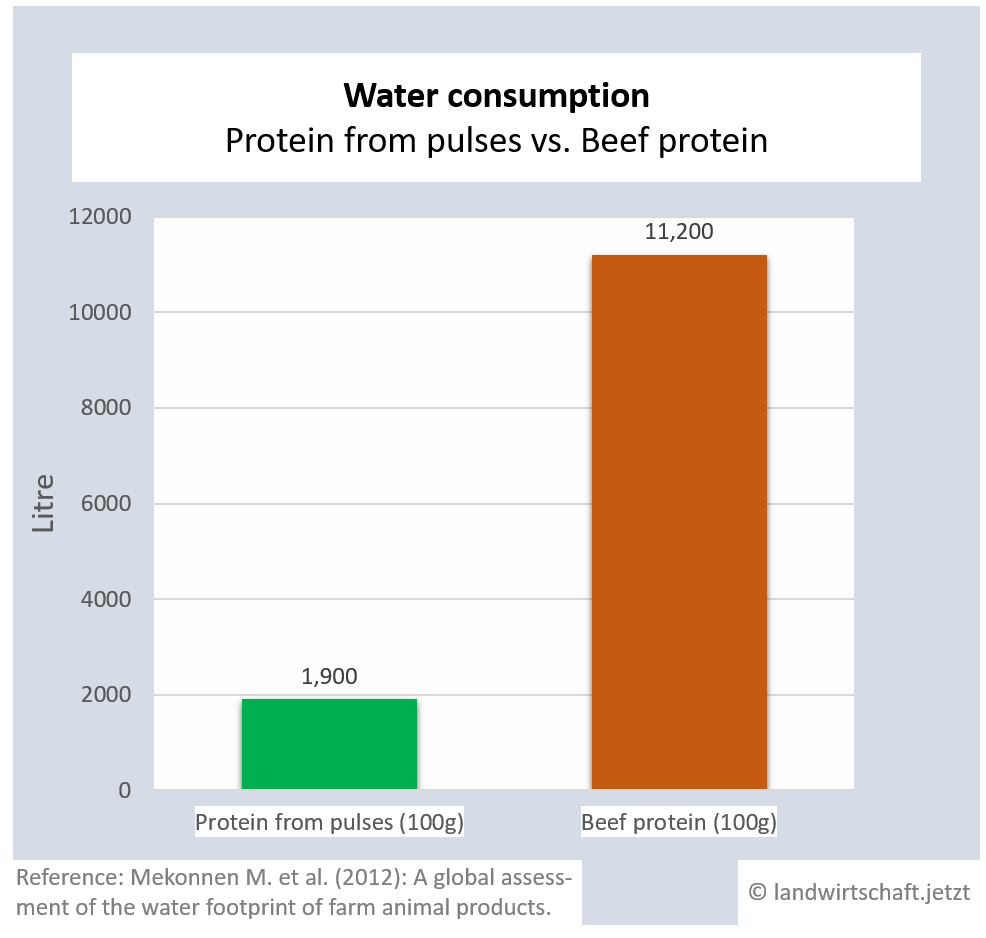
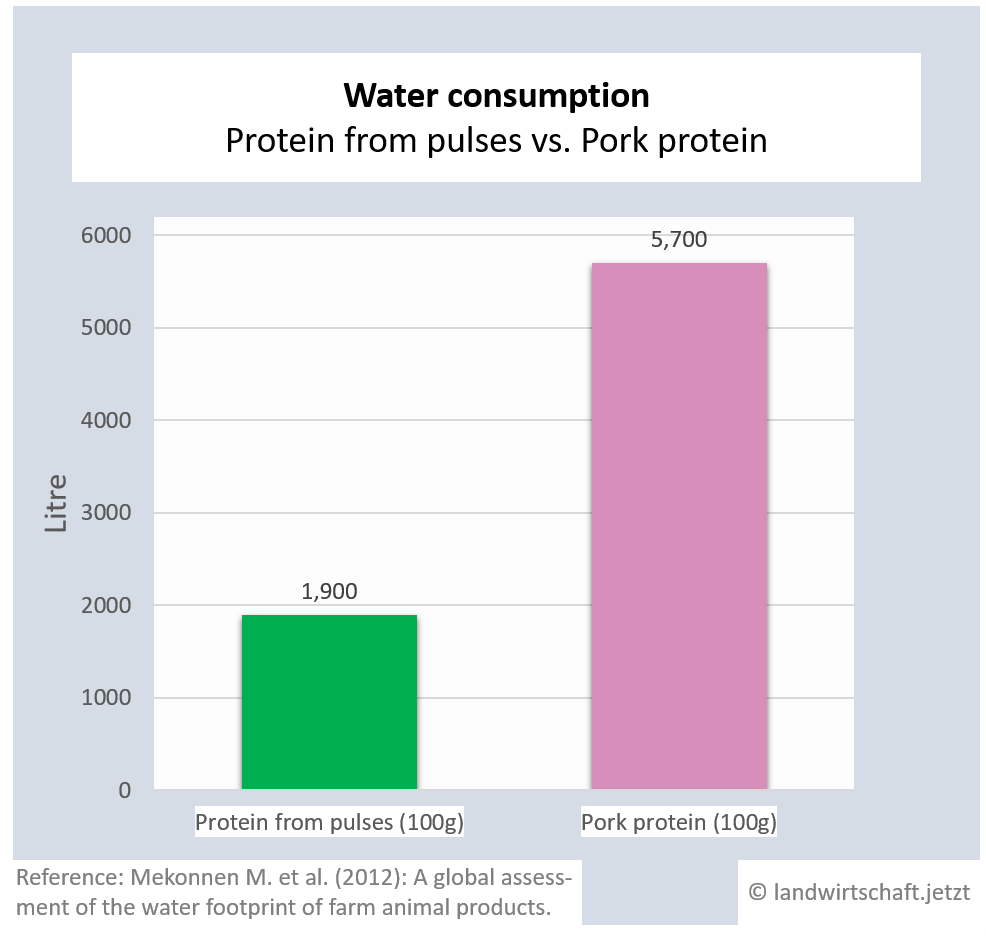
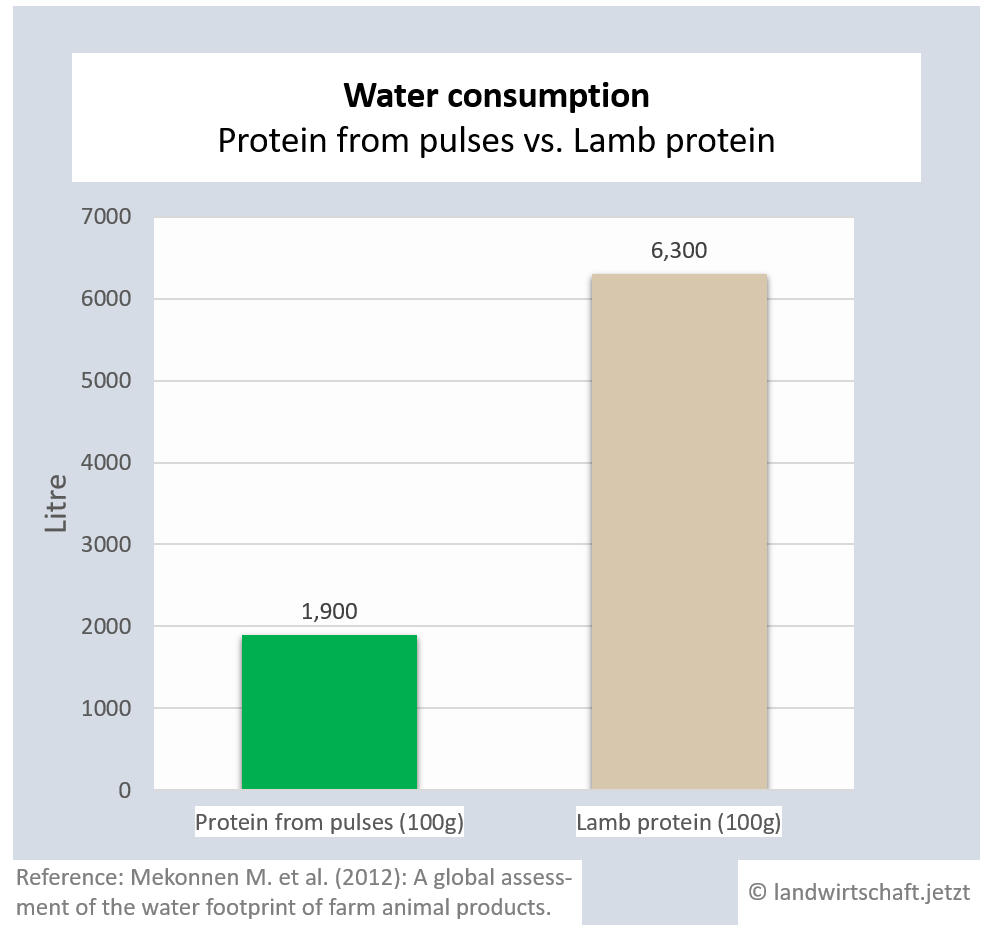
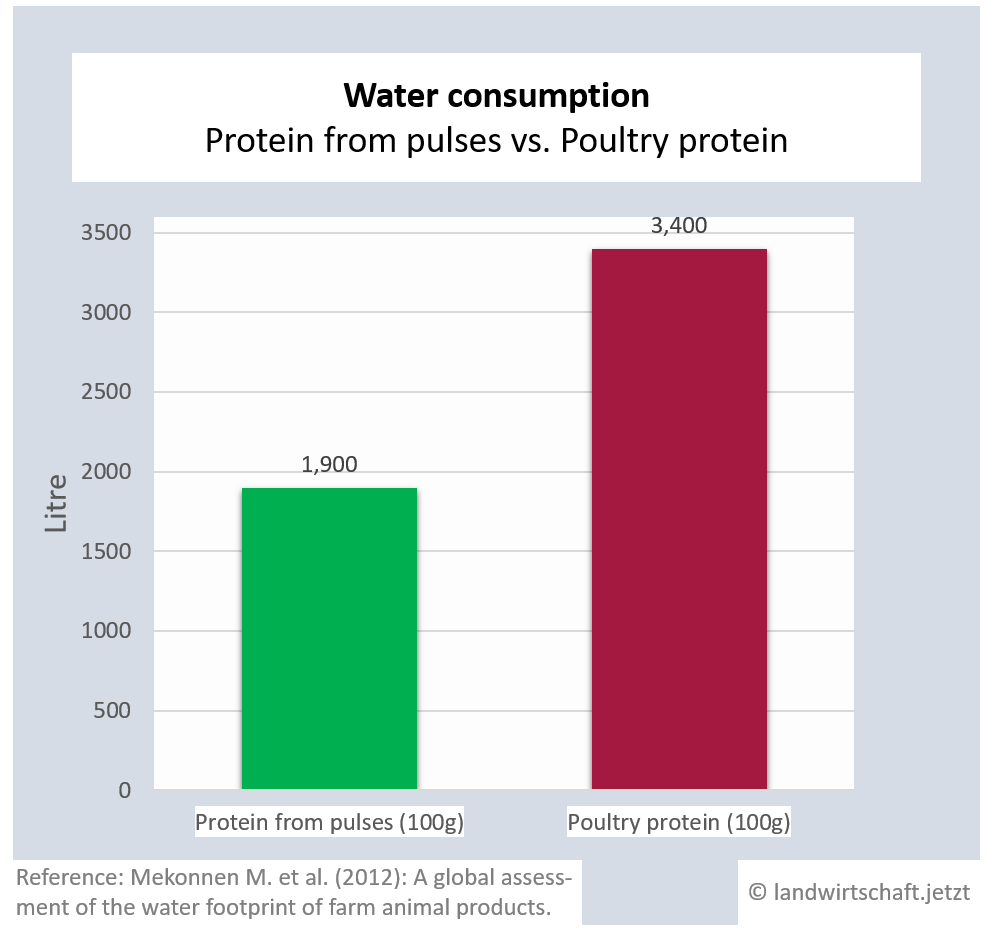
(1.1.2) Water
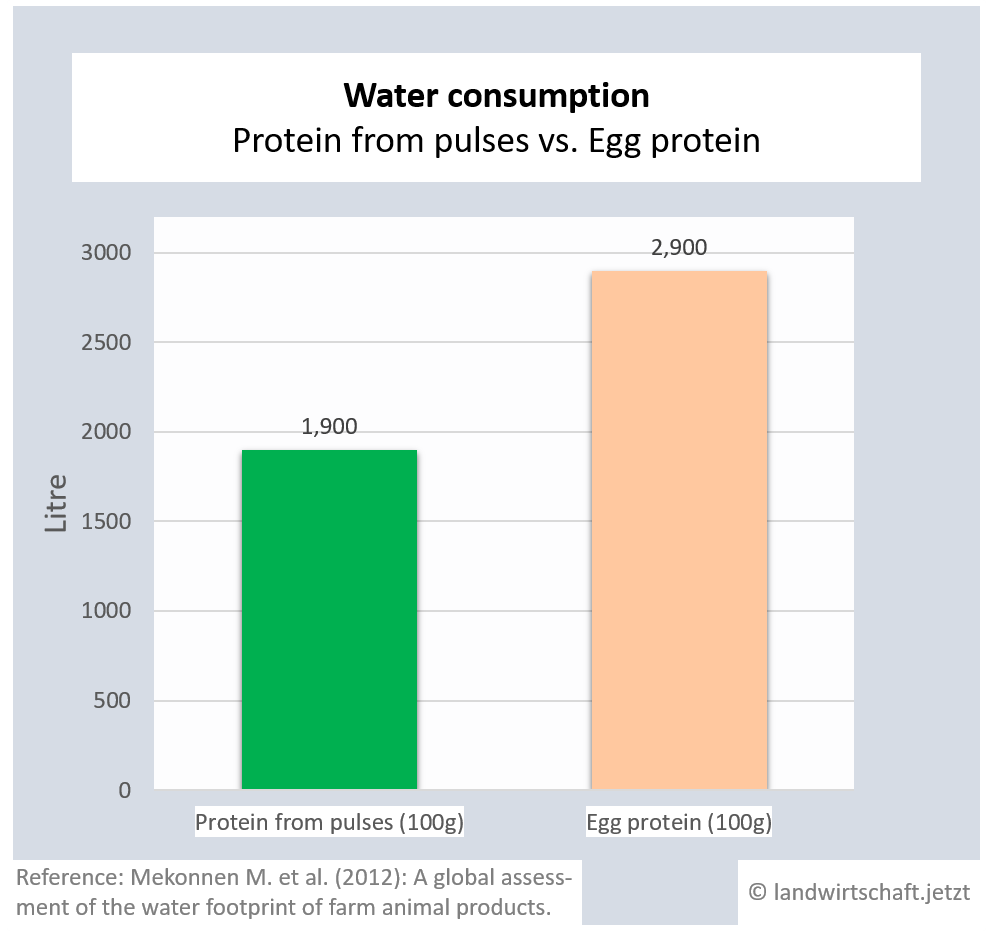
The production of one unit of beef protein requires 6 times more water than the production of an equivalent unit of protein from legumes. For pork and lamb the ratio is 3:1. Chicken protein requires 79% more water than the production of equivalent protein from legumes, proteins from eggs require 53% more water and proteins from milk require 63% more water ([18], p. 409).
(1.1.3) Chemical fertilizer
Um die hohen Futtermittelerträge zu erzielen wird zusätzlich zu Gülle und Schlachtabfällen in großem Maßstab Kunstdünger ausgebracht. In Deutschland ist mehr als die Hälfte (56%) des Hauptdüngemittels Stickstoff Kunstdünger ([13], S.63), der über das besonders energieintensive Haber-Bosch-Verfahren hergestellt wird.
(1.2) Emissions
Der hohe Stoffeinsatz in der Tierhaltung hat wiederum einen erhöhten Ausstoß an Stoffwechselprodukten wie Methan, Kohlenstoffdioxid, Distickstoffmonoxid, Ammoniak, Nitraten, Stickstoffoxiden und Phosphaten zur Folge.
(1.2.1) Greenhouse gases
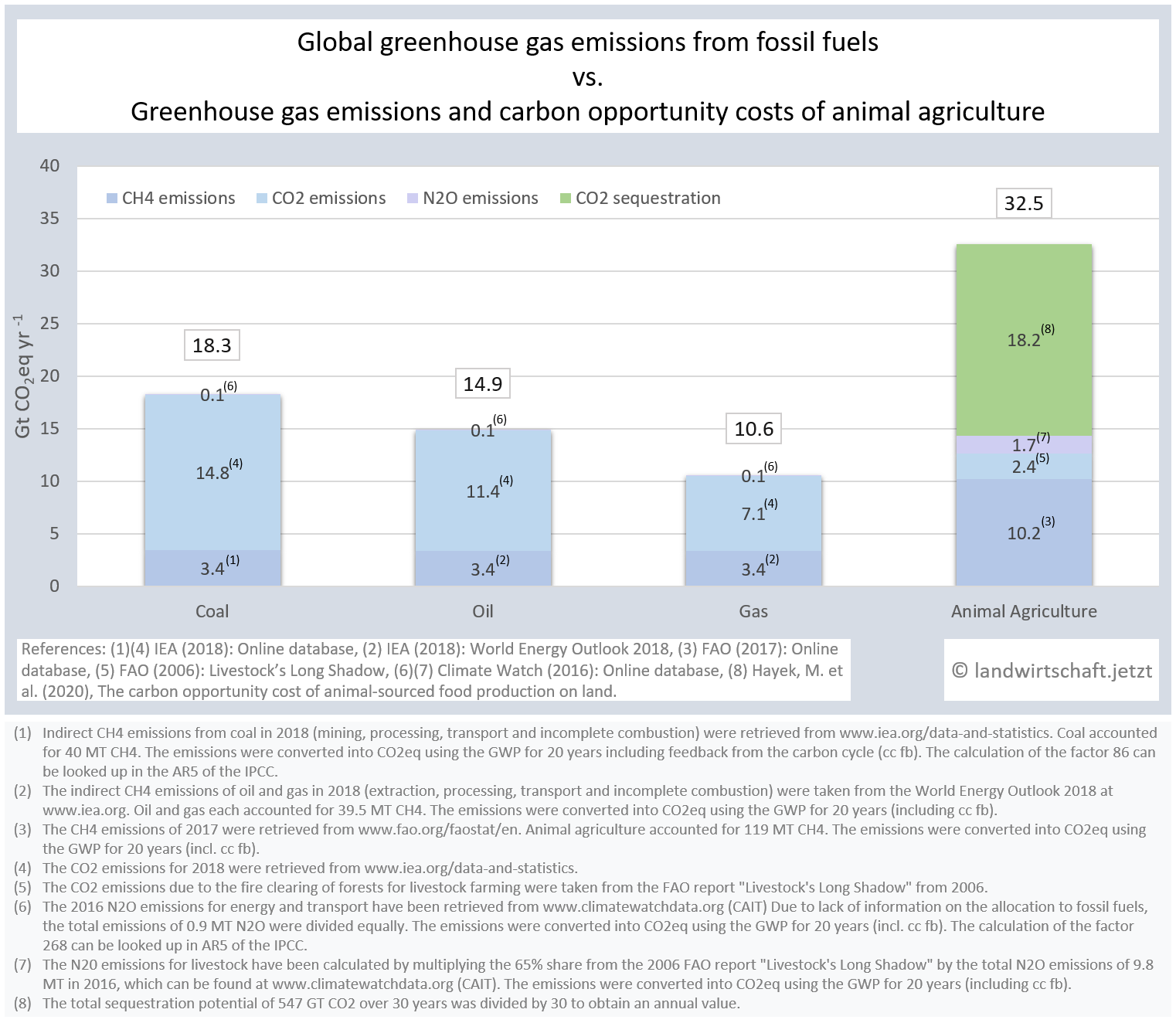
Animal husbandry is a major contributor to climate change, particularly due to the high greenhouse gas potentials of methane and nitrous oxide, deforestation and the opportunity costs of unutilised carbon sinks. The share is at least 28%. A direct comparison of greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels [33] and greenhouse gas emissions and carbon opportunity costs [32] of animal husbandry illustrate the harmfulness of agriculture with animal husbandry to the climate.
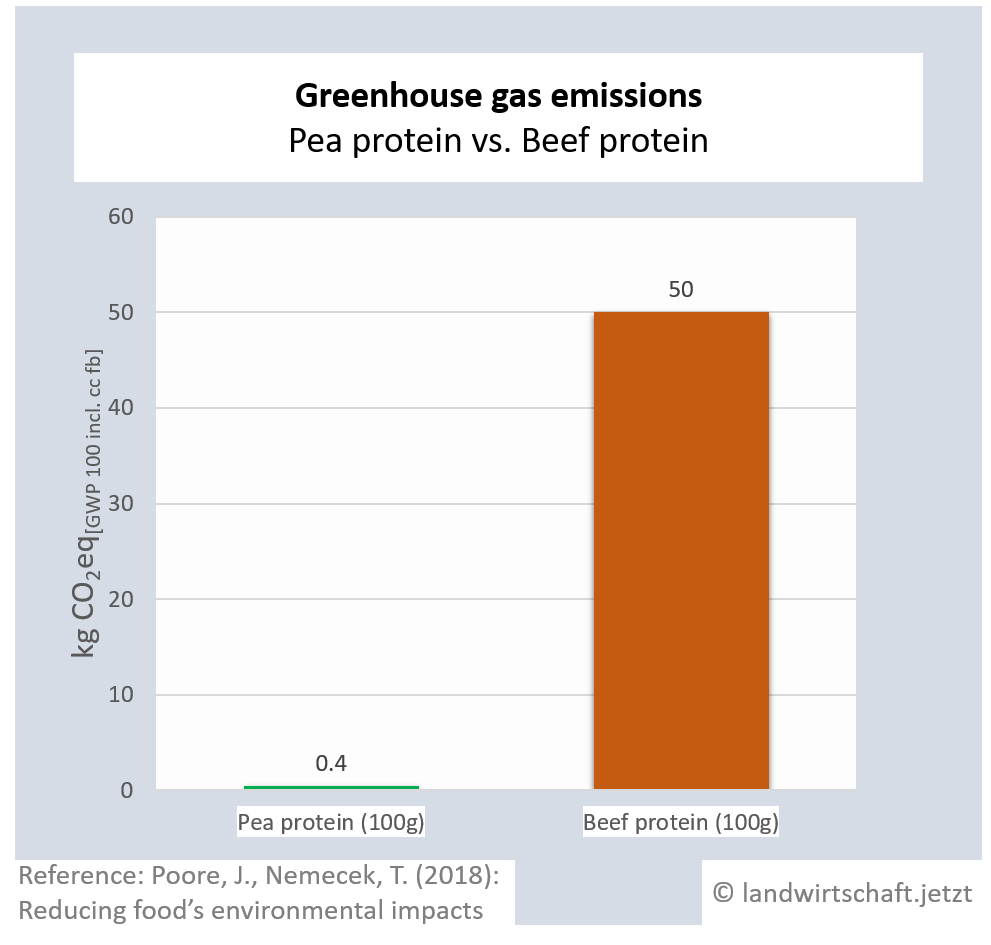
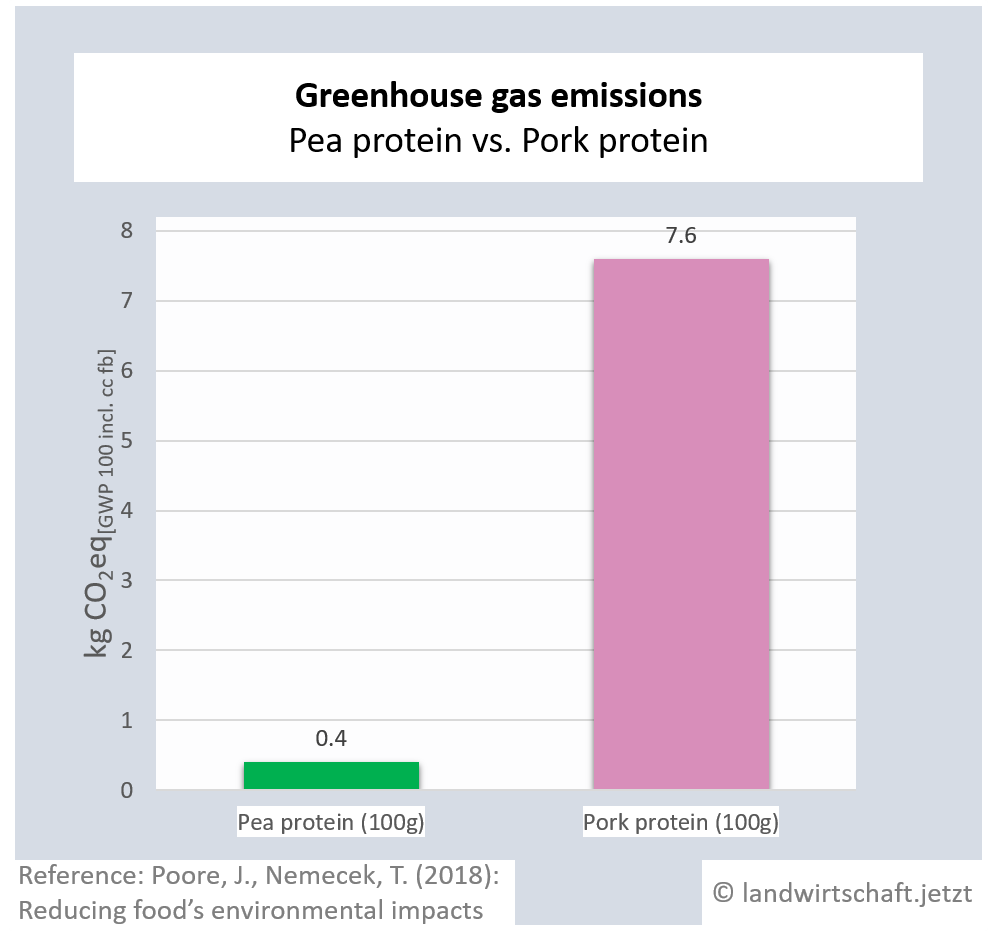
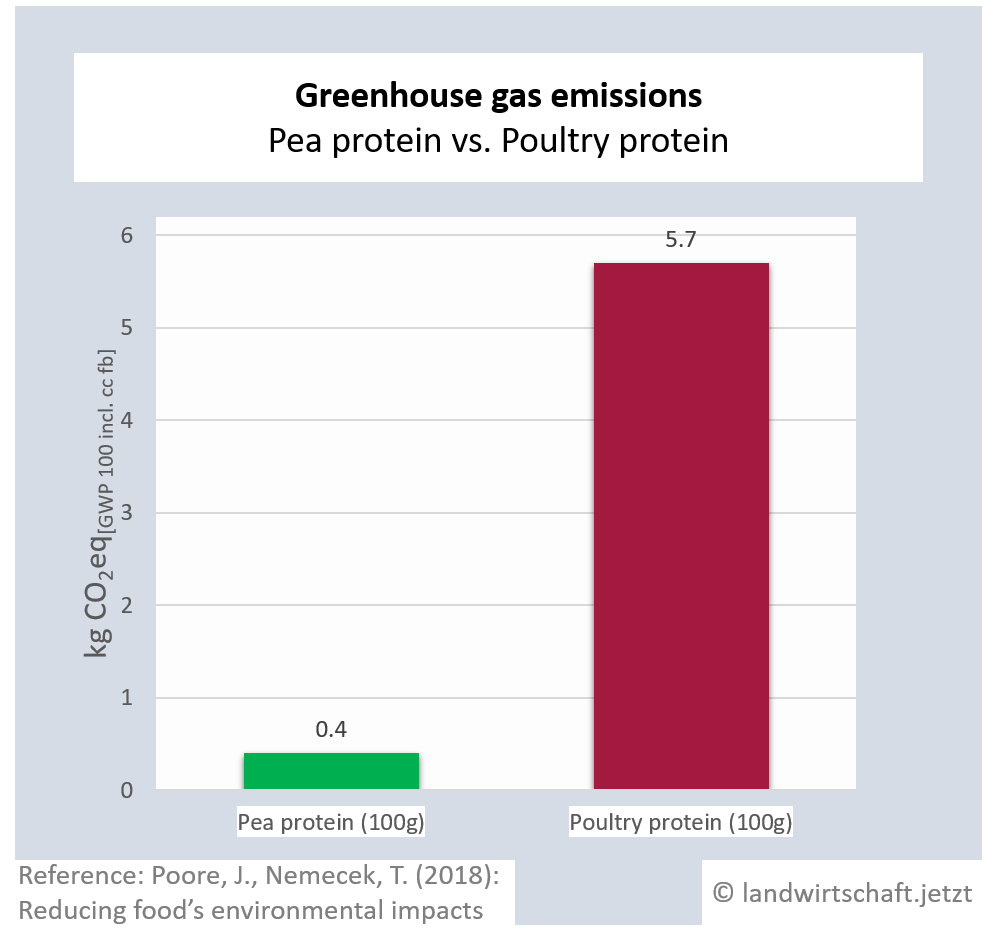
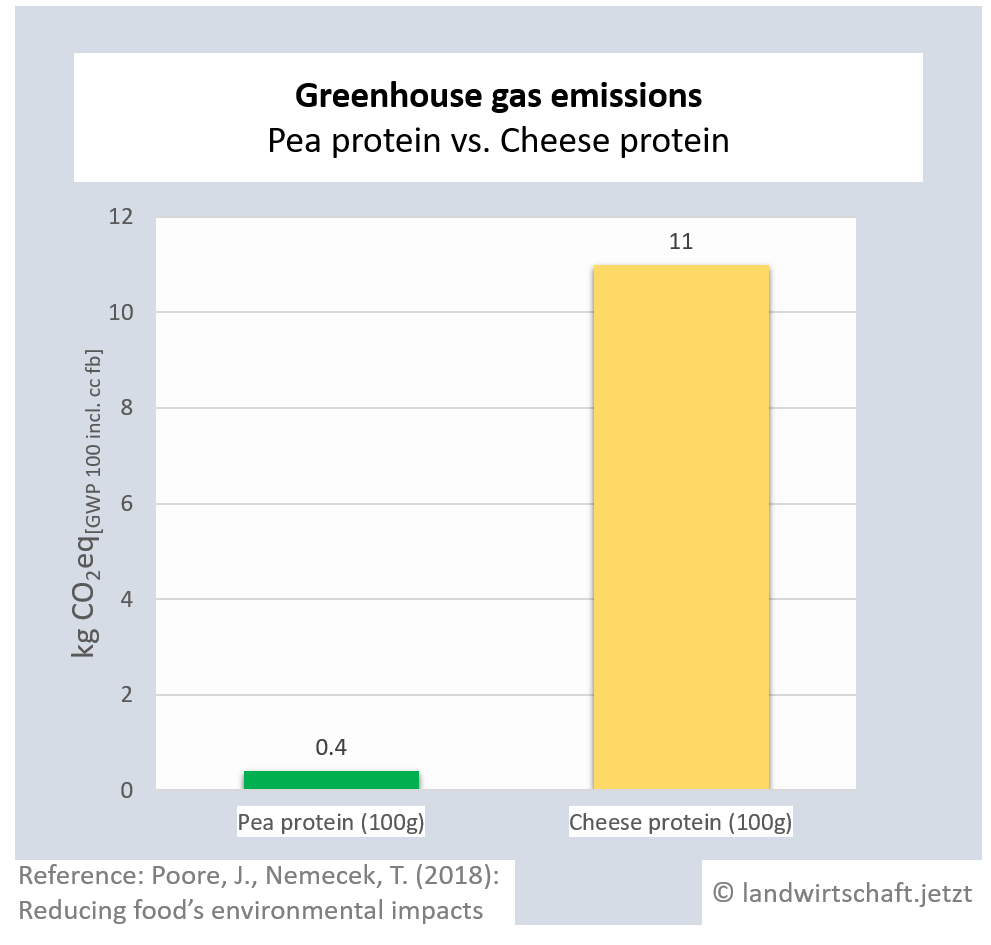
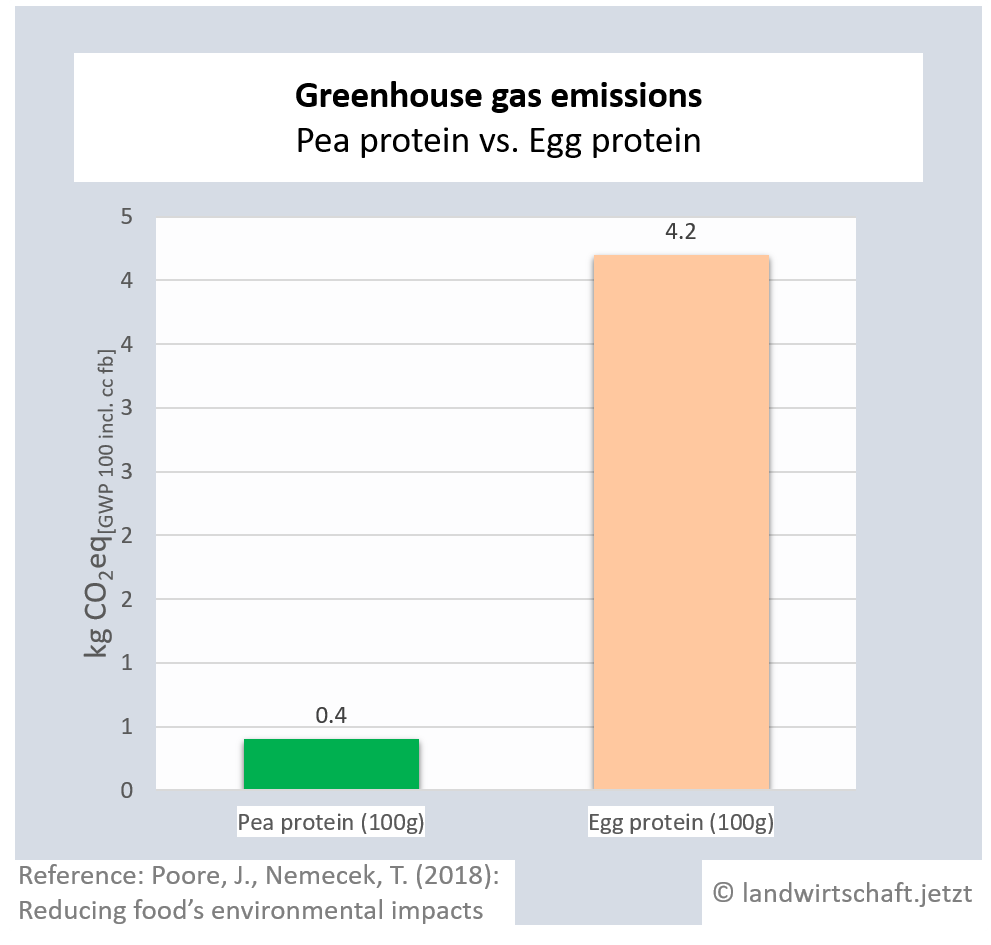
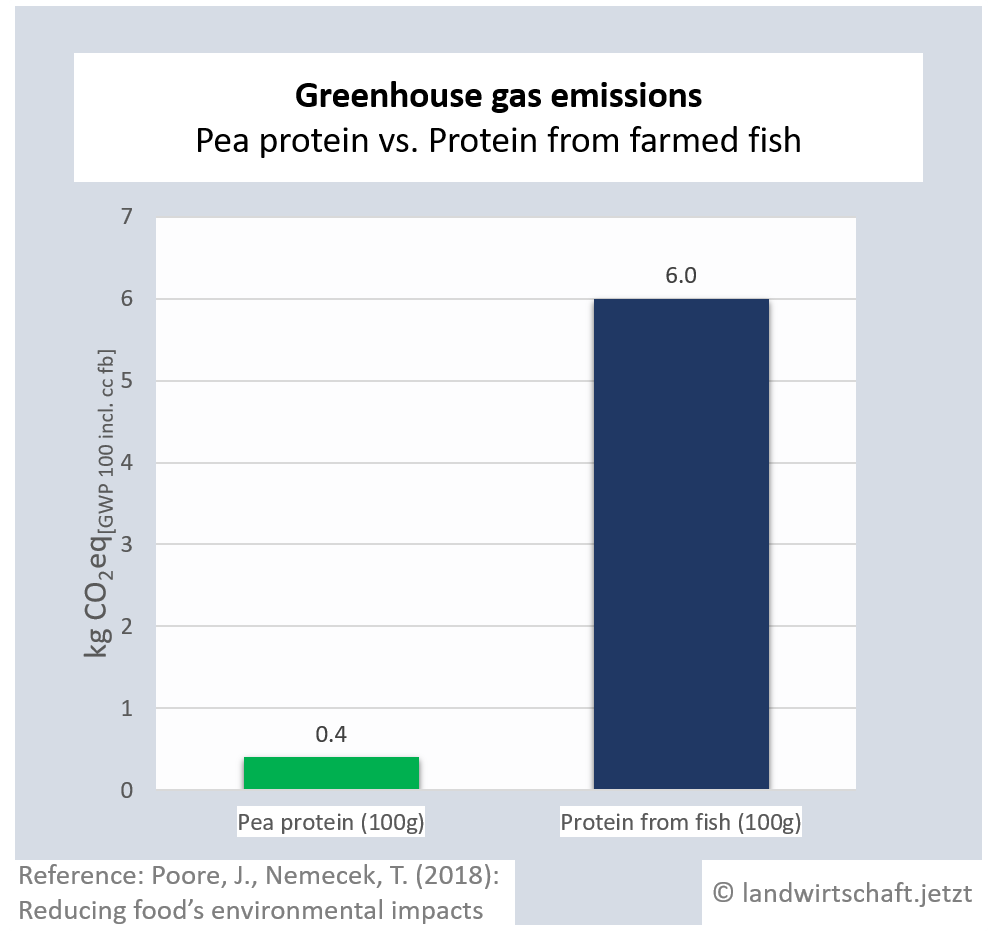
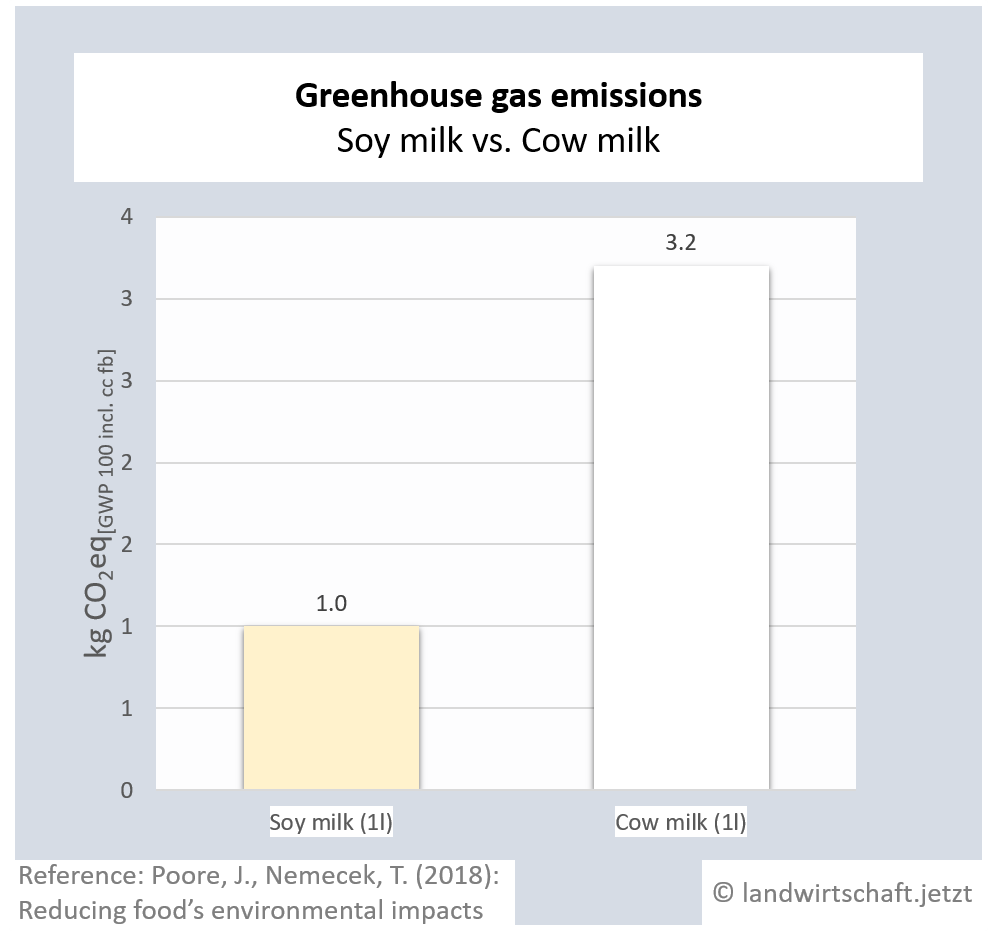
The production of one unit of protein from beef emits 125 times more greenhouse gas equivalents than the production of an equivalent unit from peas. For pork, the ratio is 19:1, for poultry 14:1, for cheese 28: 1, for eggs 11:1, for fish (farmed) 15:1 and for crustaceans (farmed) 45:1. For cow's milk, 3 times more greenhouse gas equivalents are produced than for soy milk [6].
(1.2.2) Acidifying gases
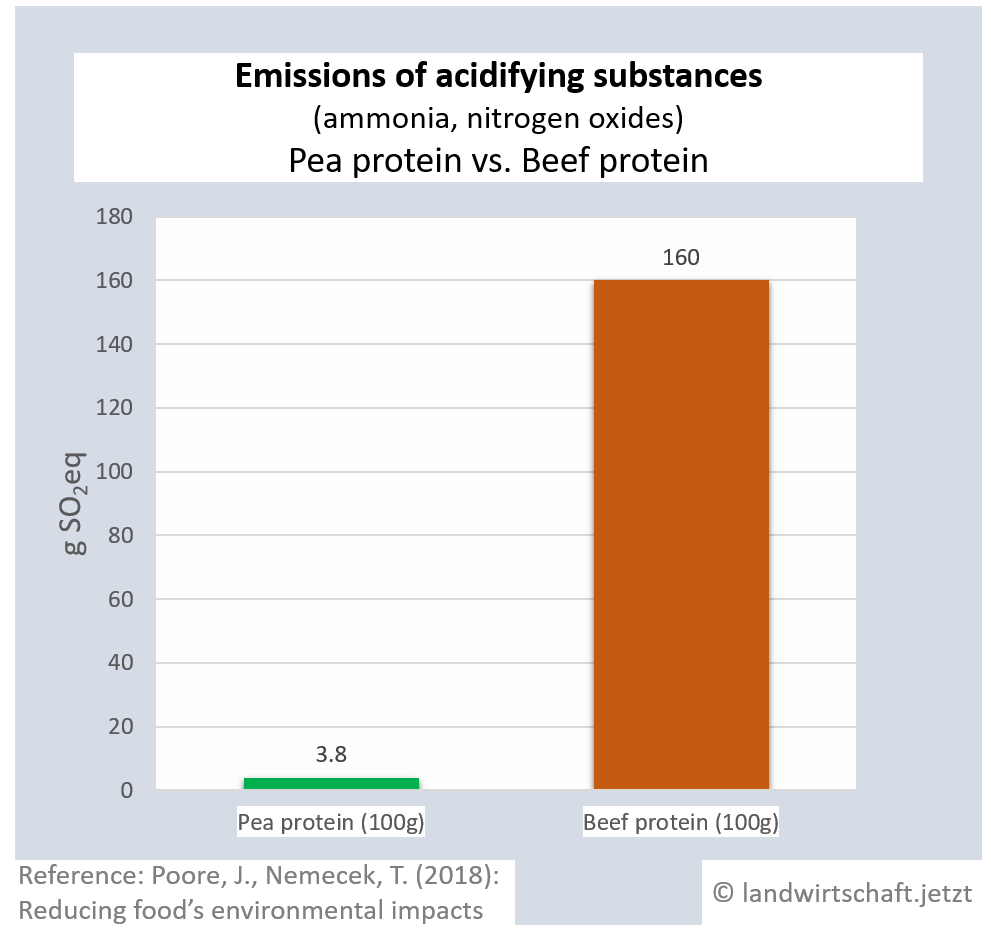
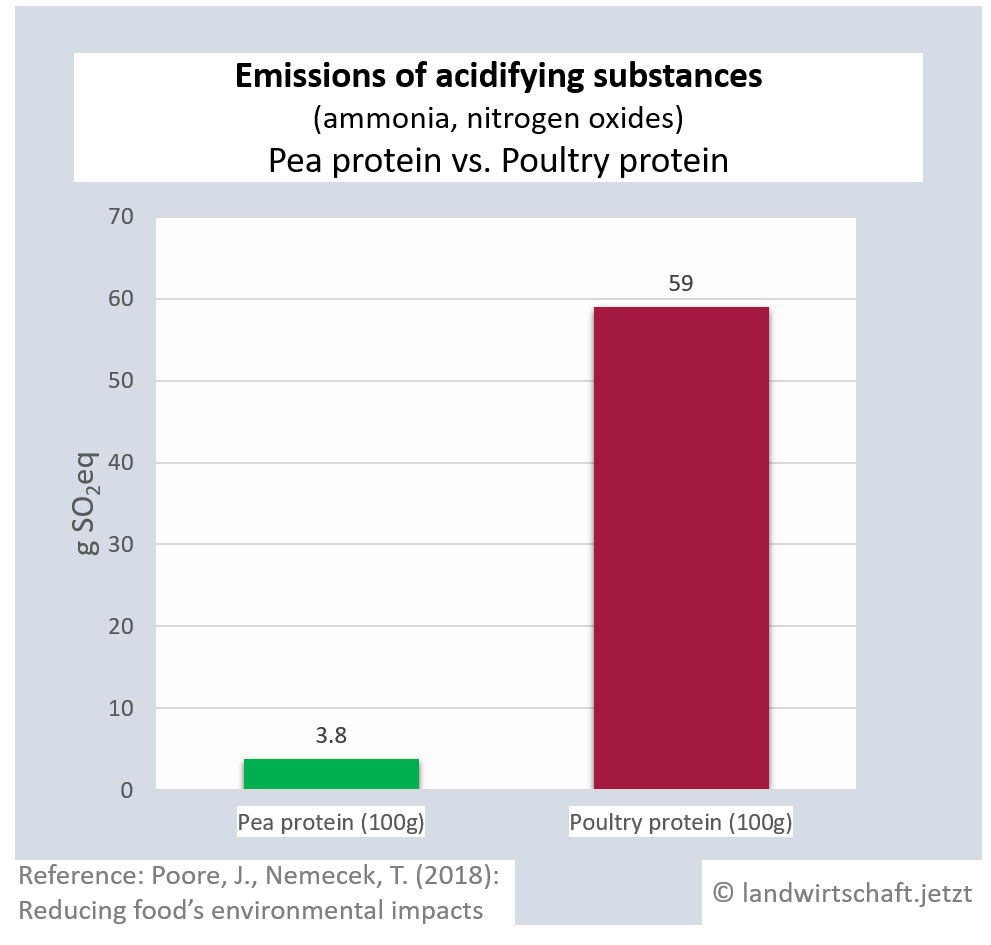
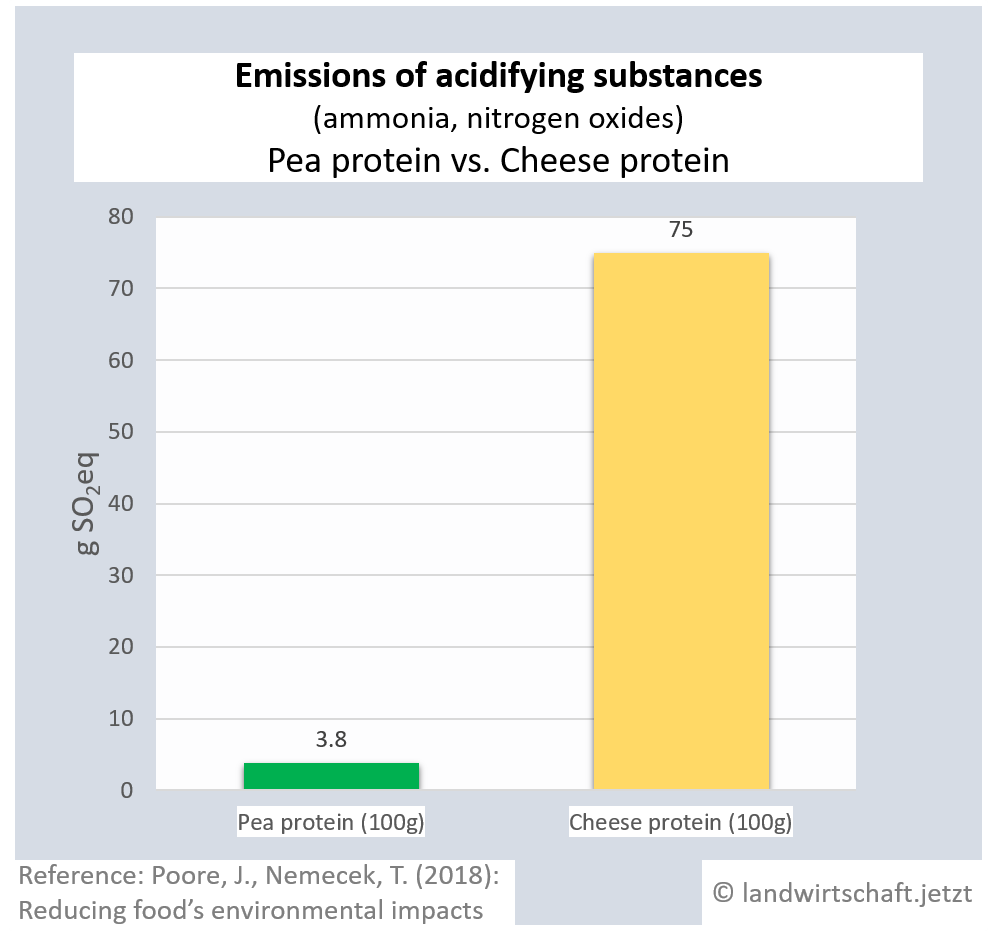
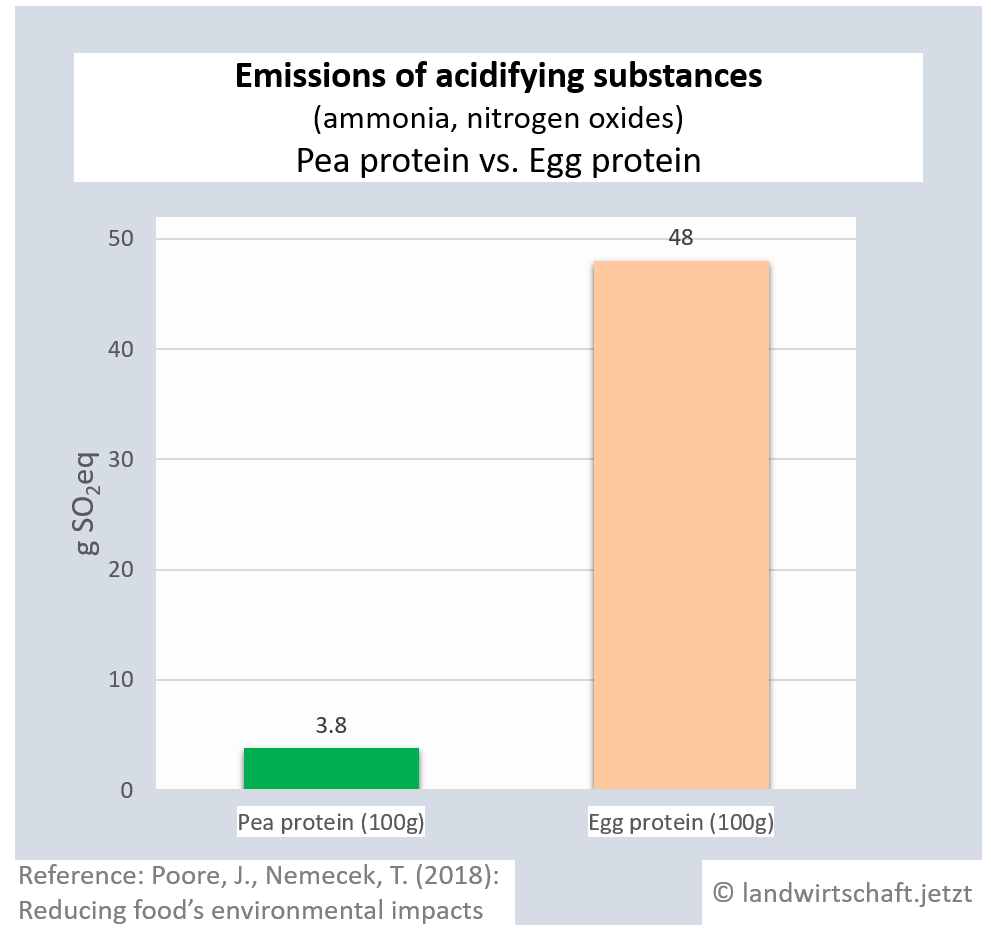
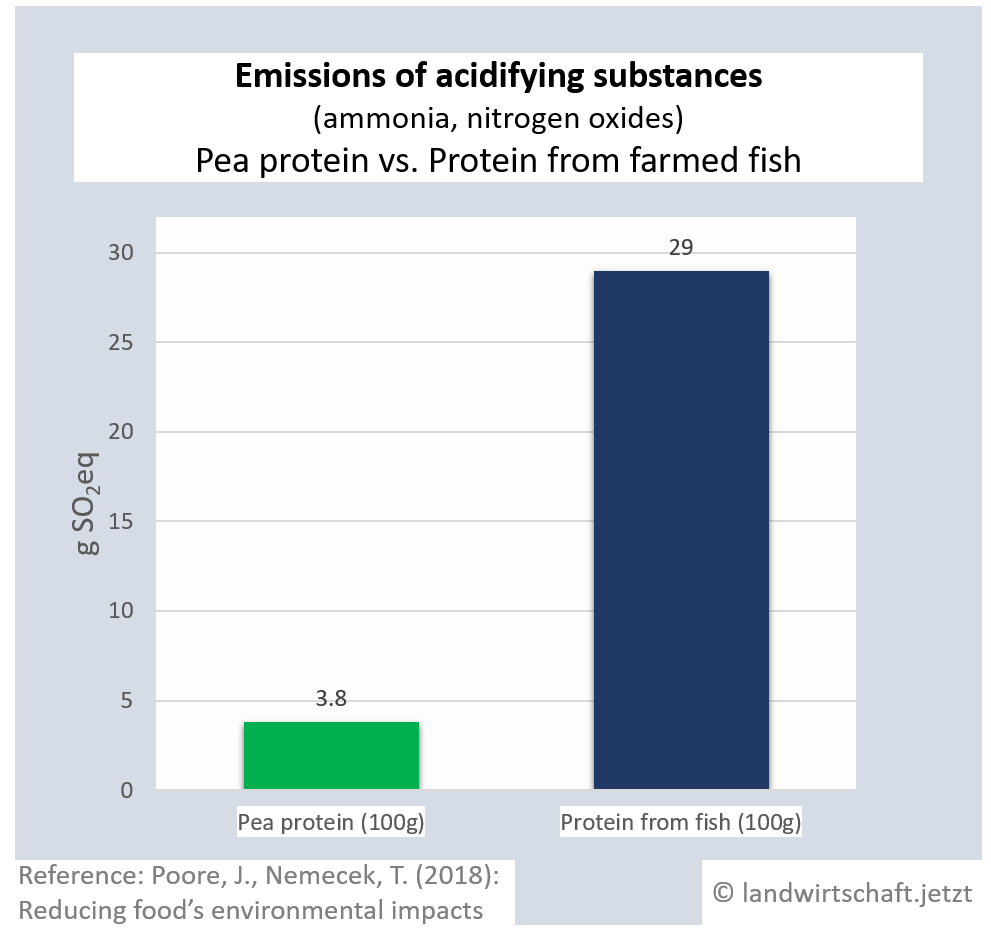
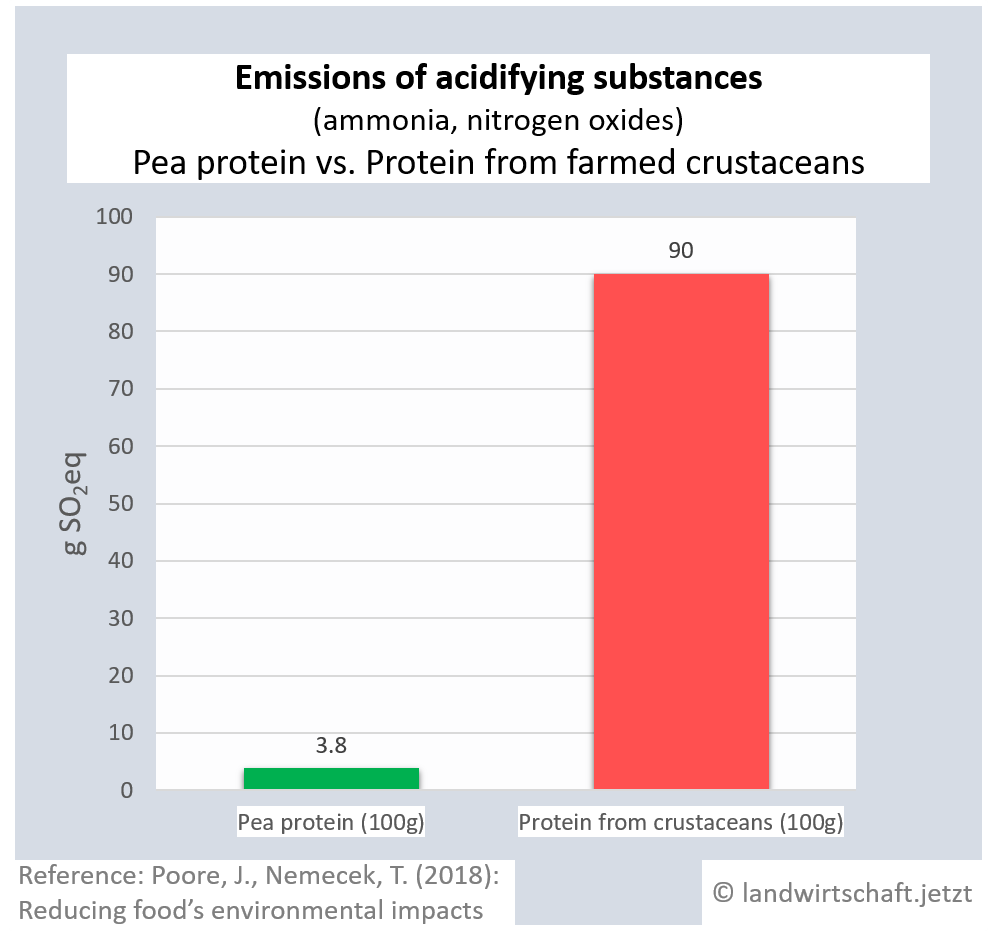
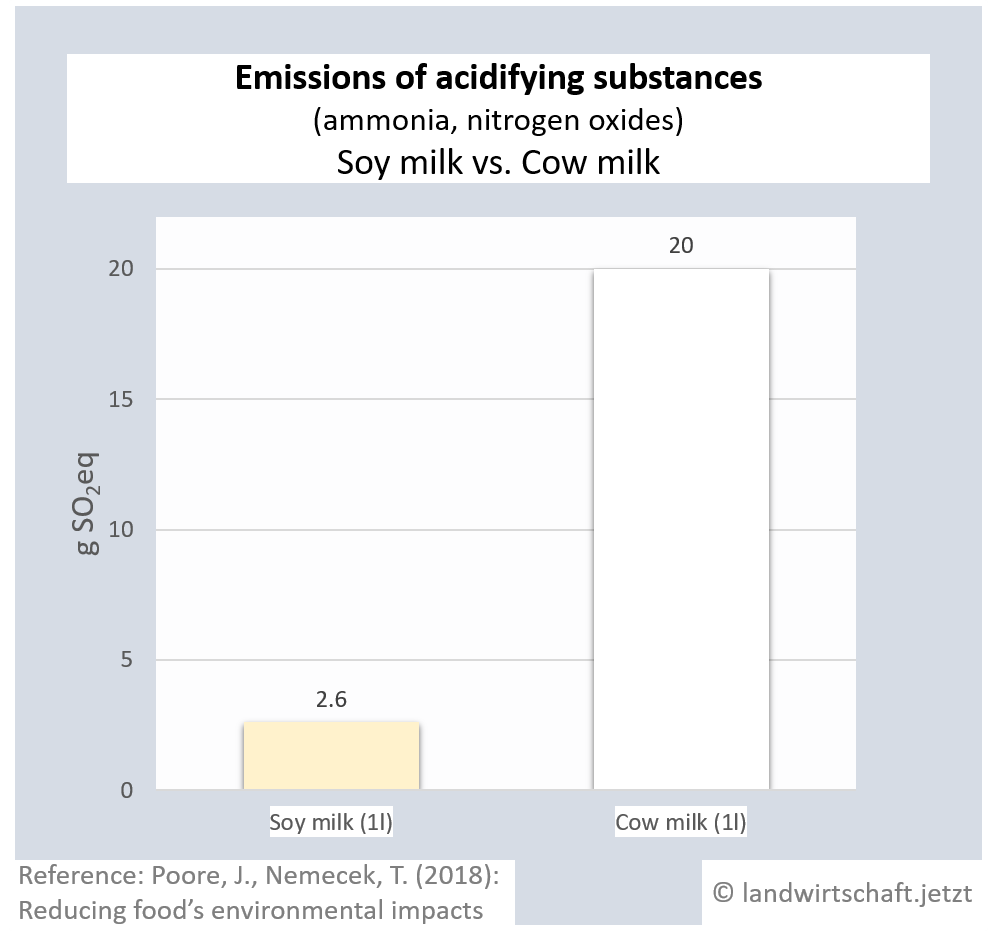
Animal husbandry results in high gas emissions of ammonia and nitrogen oxides. By eventually raining off, they enter all ecosystems, causing them to acidify. The acid stress leads to a reduction in plant vitality via an unbalanced supply of nutrients and results in lower plant resistance to drought and frost. In addition, species composition changes. Production of a unit of protein from beef emits 42 times more acidifying gases than production of an equivalent unit from peas. For pork, the ratio is 23:1, for poultry 16:1, for cheese 20:1, for eggs 13:1, for fish (farmed) 8:1 and for crustaceans (farmed) 24:1. Cow's milk produces 8 times more acidifying gases than soy milk [19]. Ammonia is also a gaseous precursor from which harmful secondary particulate matter is formed ([13], p.107).
(1.2.3) Eutrophying substances
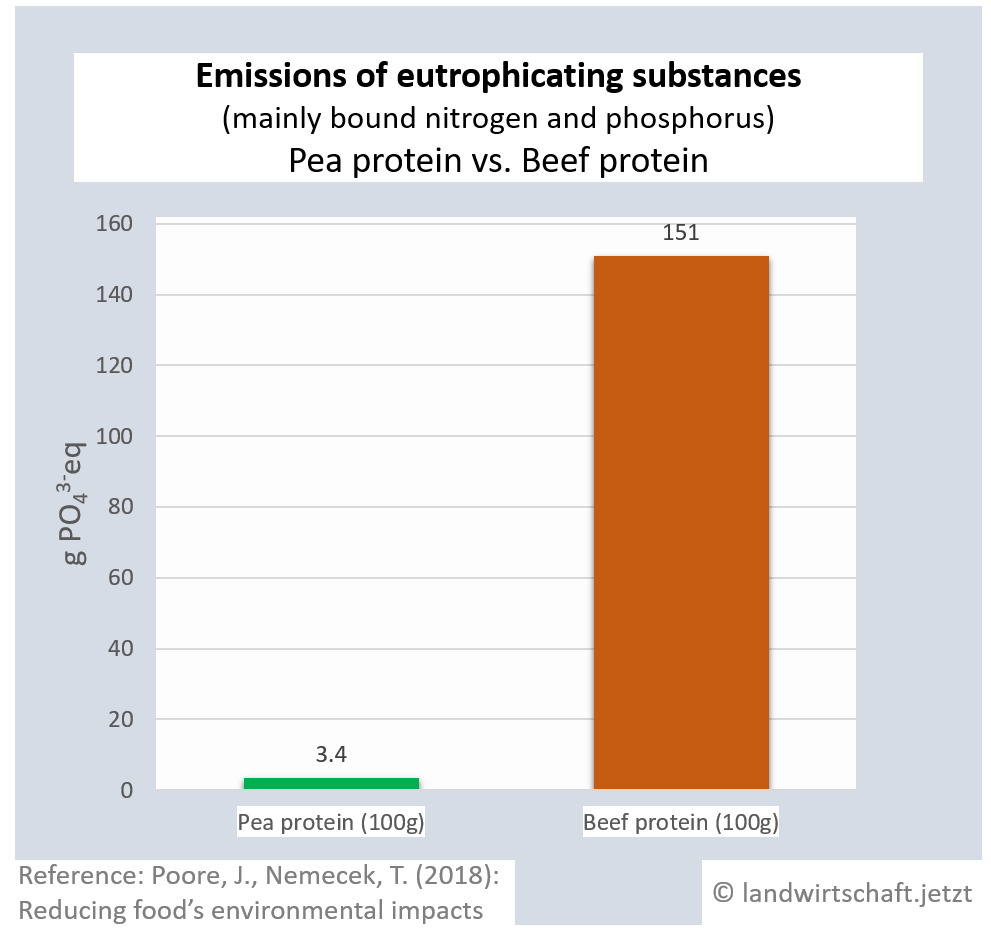
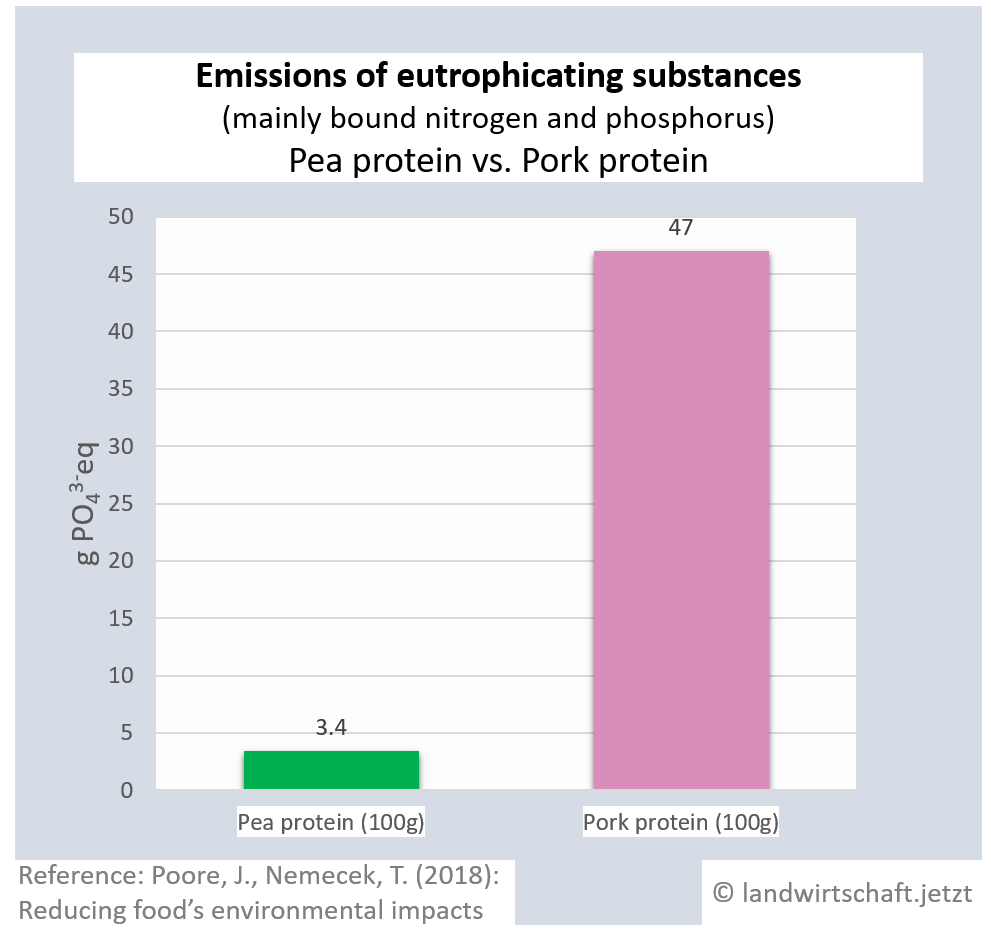
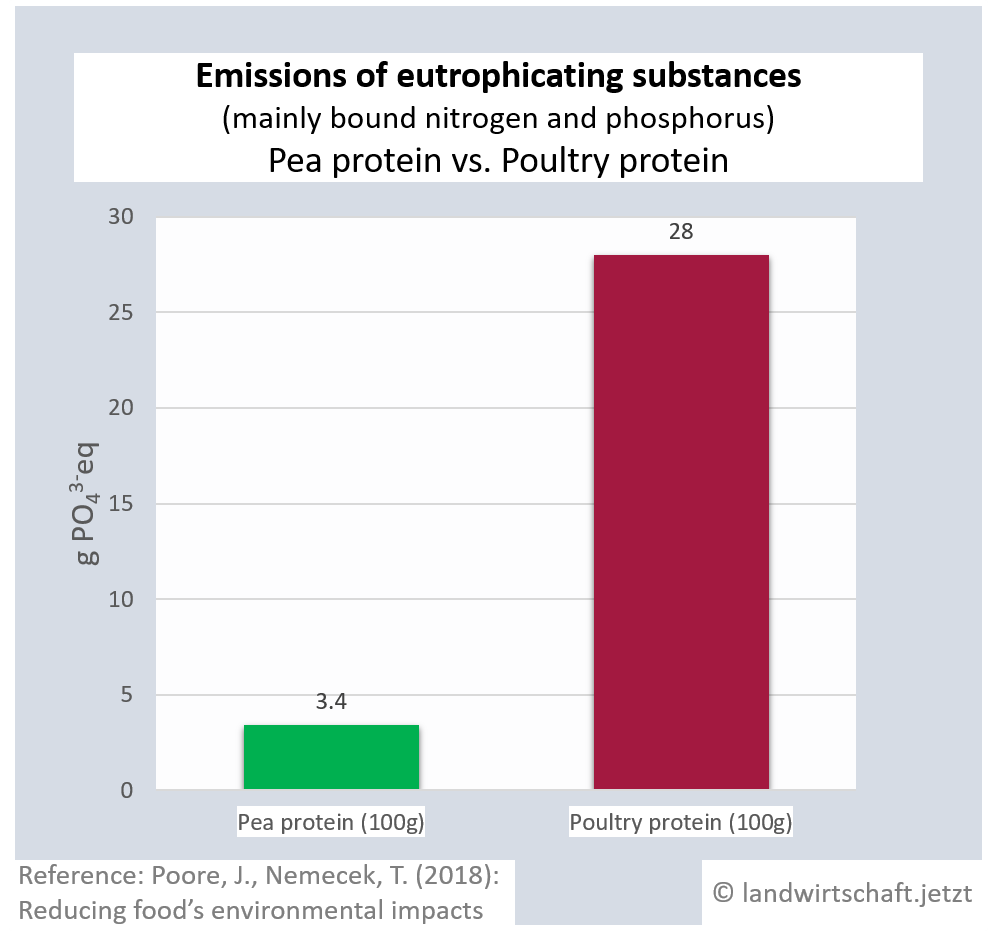
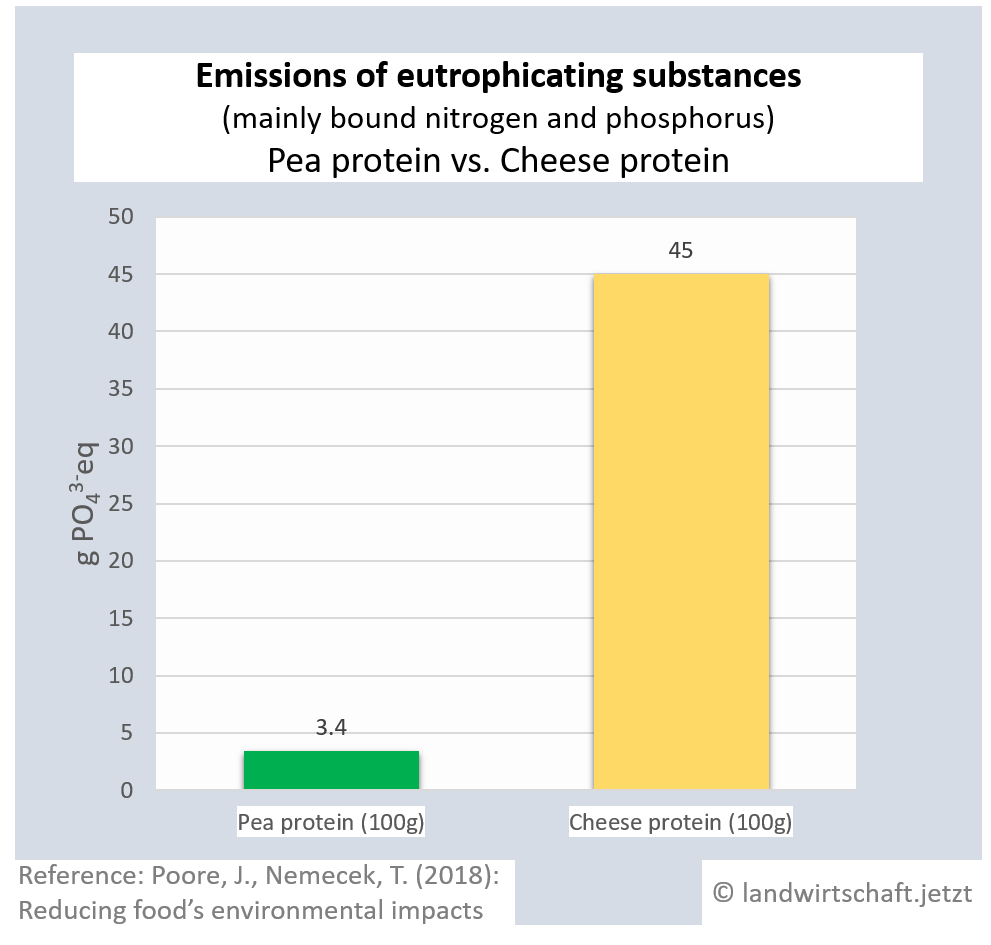
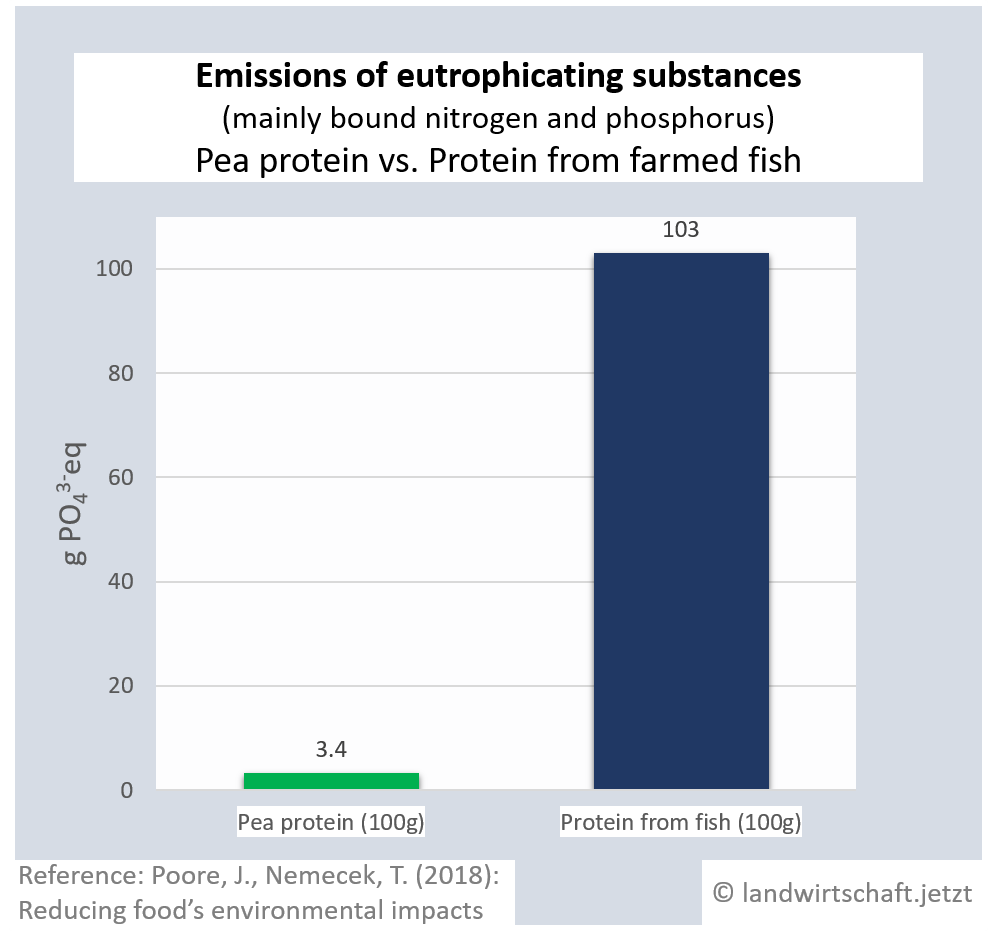
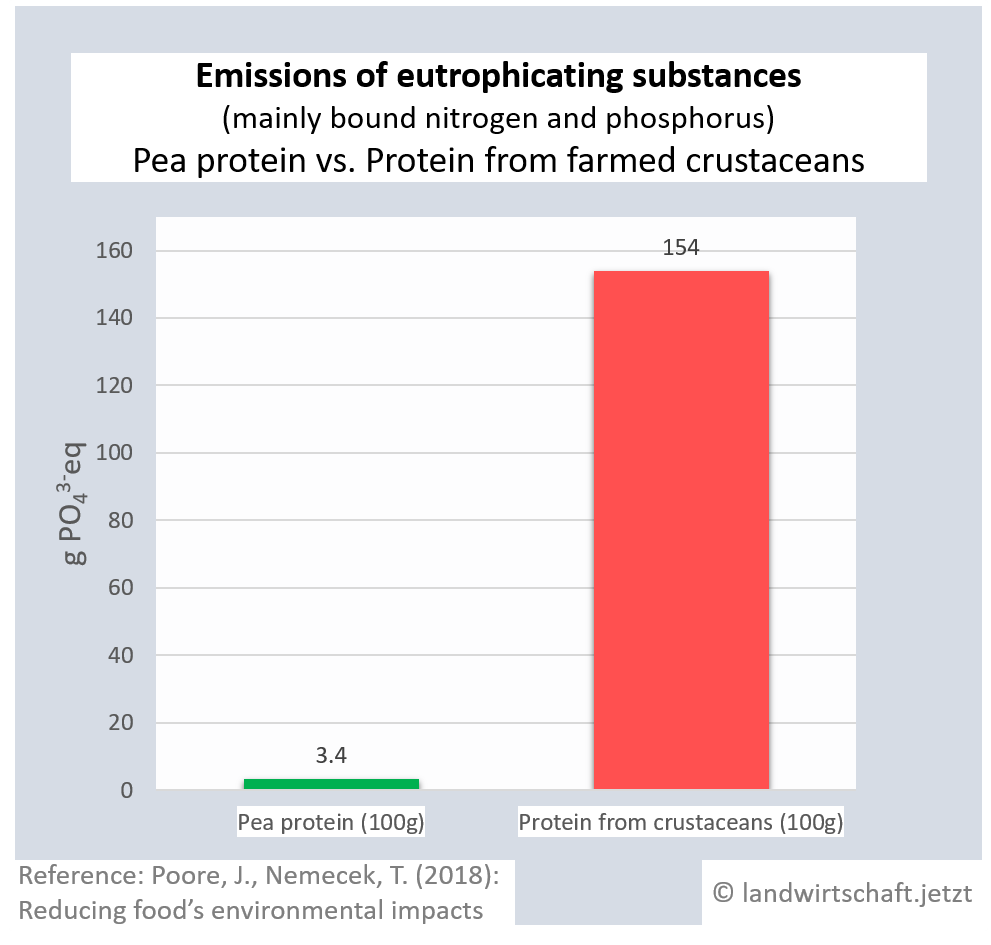
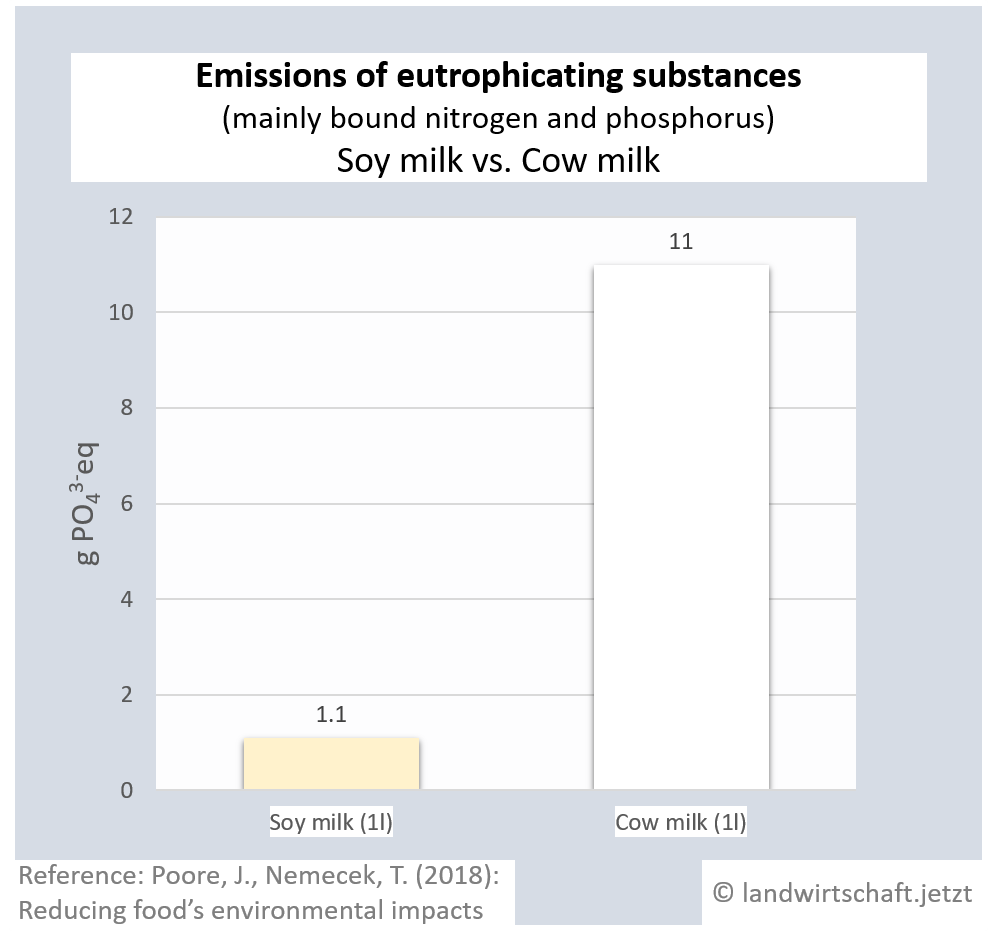
The input of liquid manure and the use of chemical fertilizers result in an oversupply of bound nitrogen and phosphorus in the ground, which causes eutrophication of waters, rivers and finally marine areas (North Sea). In large parts of northern Bavaria, the inputs permanently exceed the load limits ([13], p.76). Eutrophication favors nutrient-loving plants, displaces nutrient-sensitive plants and thus leads to a loss of biodiversity in plants, insects and animals. In lakes and seas, complete ecosystems collapse. The production of one unit of protein from beef results in 44 times higher inputs of eutrophicating substances than the production of a corresponding unit from peas. For pork, the ratio is 14:1, for poultry 8:1, ffor cheese 13: 1, ffor eggs 6:1, for fish (farmed) 30:1 and for crustaceans (farmed) 45:1. Cow's milk releases 10 times more euthrophying substances into the surface water than soy milk [19].
(2) Use of herbicides, fungicides and insecticides.
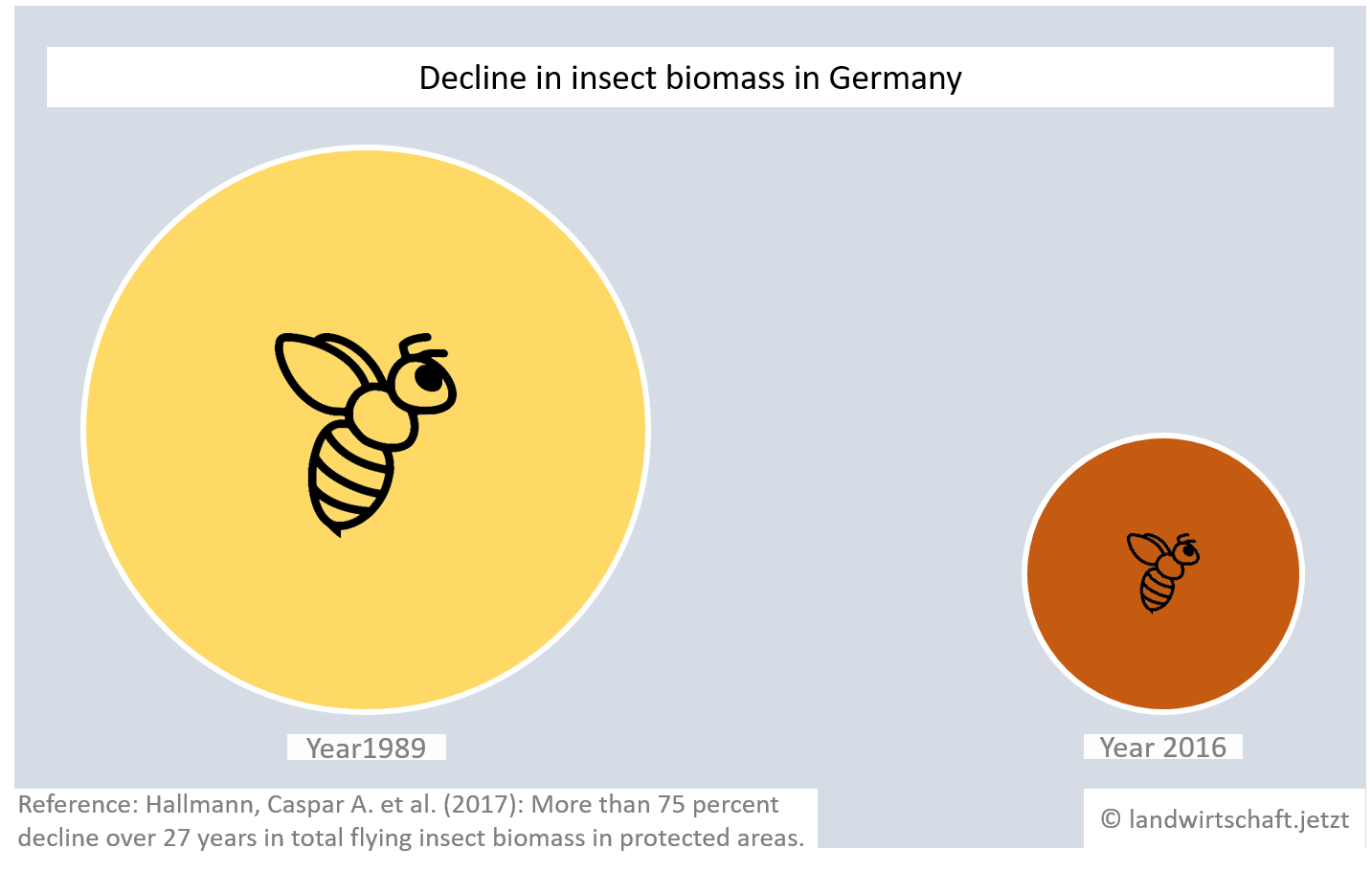
The high demand for animal feed for livestock and fishing requires intensification of agriculture using herbicides, fungicides and insecticides. In Germany, such agents with more than 32 thousand tons of active ingredient ([13], p.54) were sold in 2016. Exact figures on their use in Bavarian agriculture are not available, but in Bavaria the limit values in groundwater were exceeded in the period 2009-2012 more than twice as often as in the whole of Germany ([37], p.33). On the one hand, herbicides, fungicides and insecticides are harmful to human health via water and food intake. On the other hand, they cause considerable damage to insect populations. [23]. The decrease in insect biomass in turn has effects on plants and animals. For example, 80% of wild plants are dependent on insects for pollination [35], while 60% of birds depend on insects as a food source [36].
Overall,
- the high demand for land and thus the displacement of plants and wildlife
- the high emissions of acidifying and eutrophying substances
- the use of pesticides and thus the loss of insects
are reasons for the loss of biodiversity that is leading to declines in plant diversity and animal populations [25] and the observable sixth mass extinction of species.
The extinction rate is 117 times higher than would be expected without human influence [24]. Most endangered species are native to South America, Asia and Oceania, but animal agriculture in Germany also bears a causal share of responsibility for the extinction events there due to the high imports of feed and the associated clearing of rainforests.
(3) Use of antibiotics
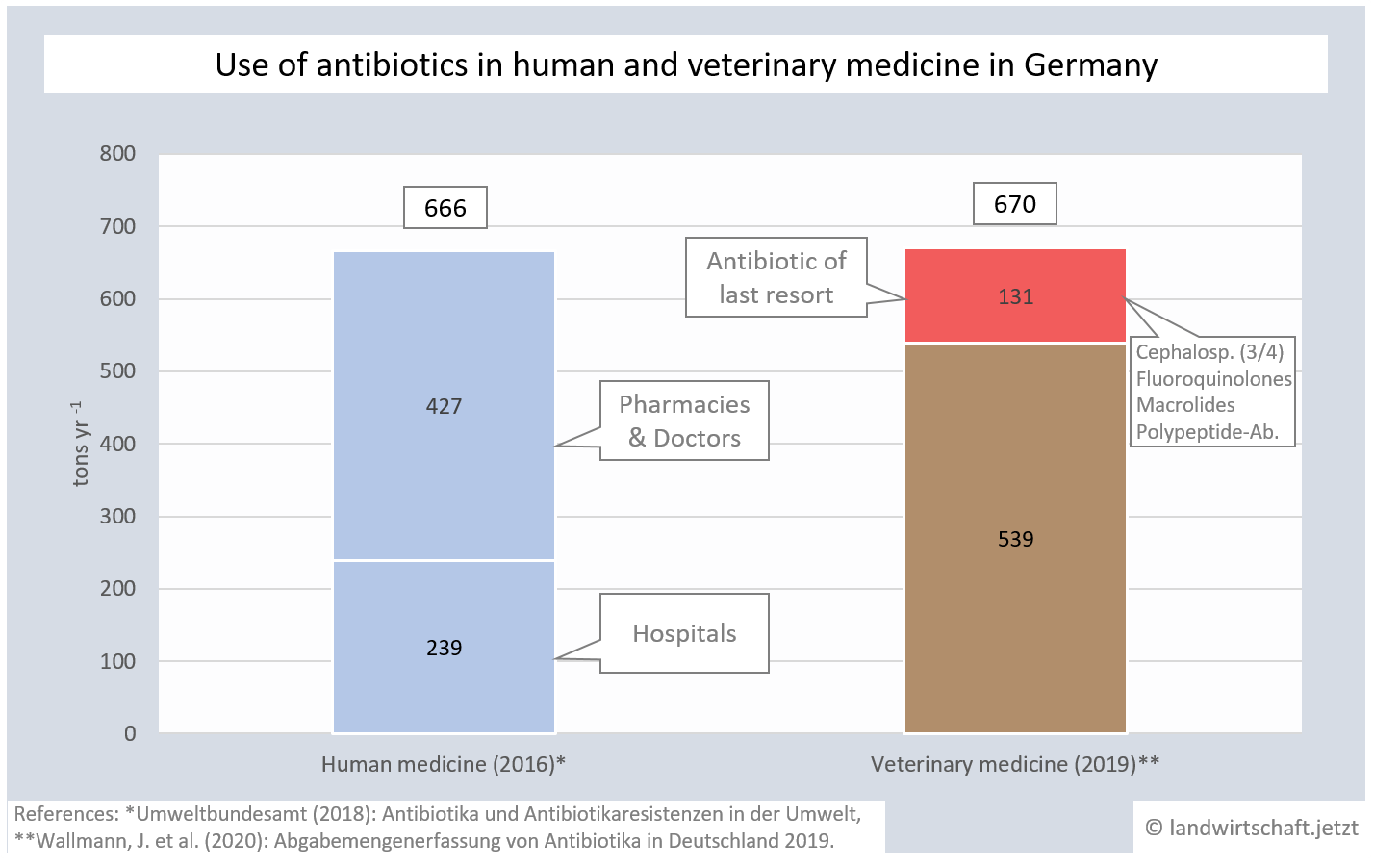
Animal agriculture requires a high level of antibiotics. They are used to a small extent against individual animal diseases, but mostly preventively and to accelerate the growth of the animals and thus their readiness for slaughter. In 2019, 670 tons of antibiotics were used in veterinary medicine in Germany, including 131 tons of antibiotics of last resort classified by the WHO (Highest Priority Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine). The proportion of use in Bavaria is above average [40]. In 2016, 666 tons of antibiotics were used in human medicine in Germany ([41], p.6).
The use of antibiotics, especially in animal agriculture, leads to dangerous antibiotic resistance, which impairs the effective treatment of infectious diseases in humans and animals. In Germany about 6000 people die of multi-resistant germs every year. The WHO classifies antibiotic resistance as one of the greatest threats to global health, food security and development [42].
(4) Cause and driver of zoonoses and pandemics
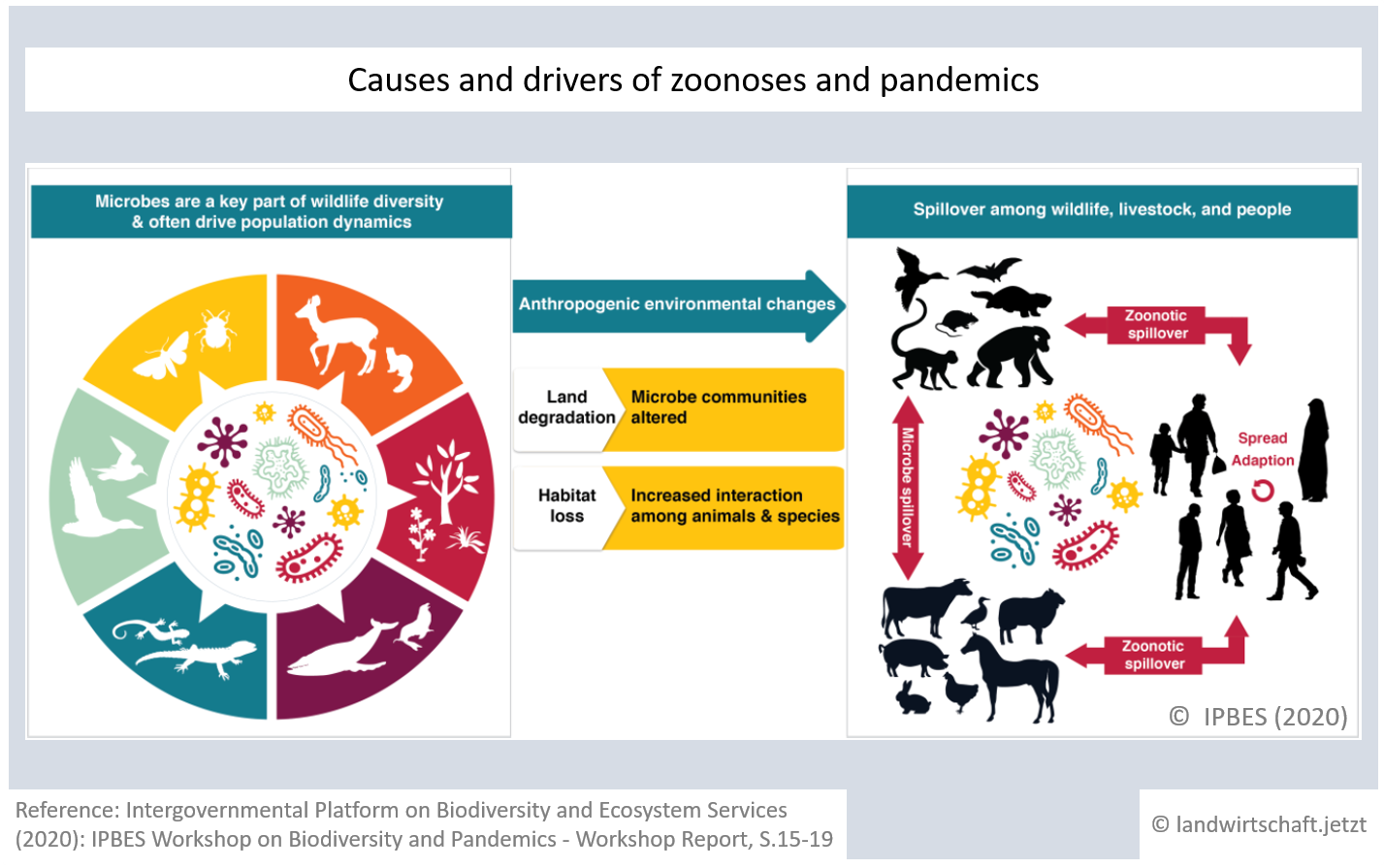
Animal agriculture, with its high density of animals and its high land requirements, is one of the main reasons for diseases transmissible from animals to humans (zoonoses) and ultimately for pandemics. The high housing densities promote the emergence of pathogens within animal husbandry and the probability of jumps to humans. The enormous land requirements of animal agriculture for feed and pasture displace wild animals from their habitats and bring them into contact with domesticated animals and humans ([38], pp.15-19). More than 70% of all new diseases occurring in humans are zoonoses ([39], p.5). Almost 100% of pandemics are caused by zoonoses ([39], p.8).
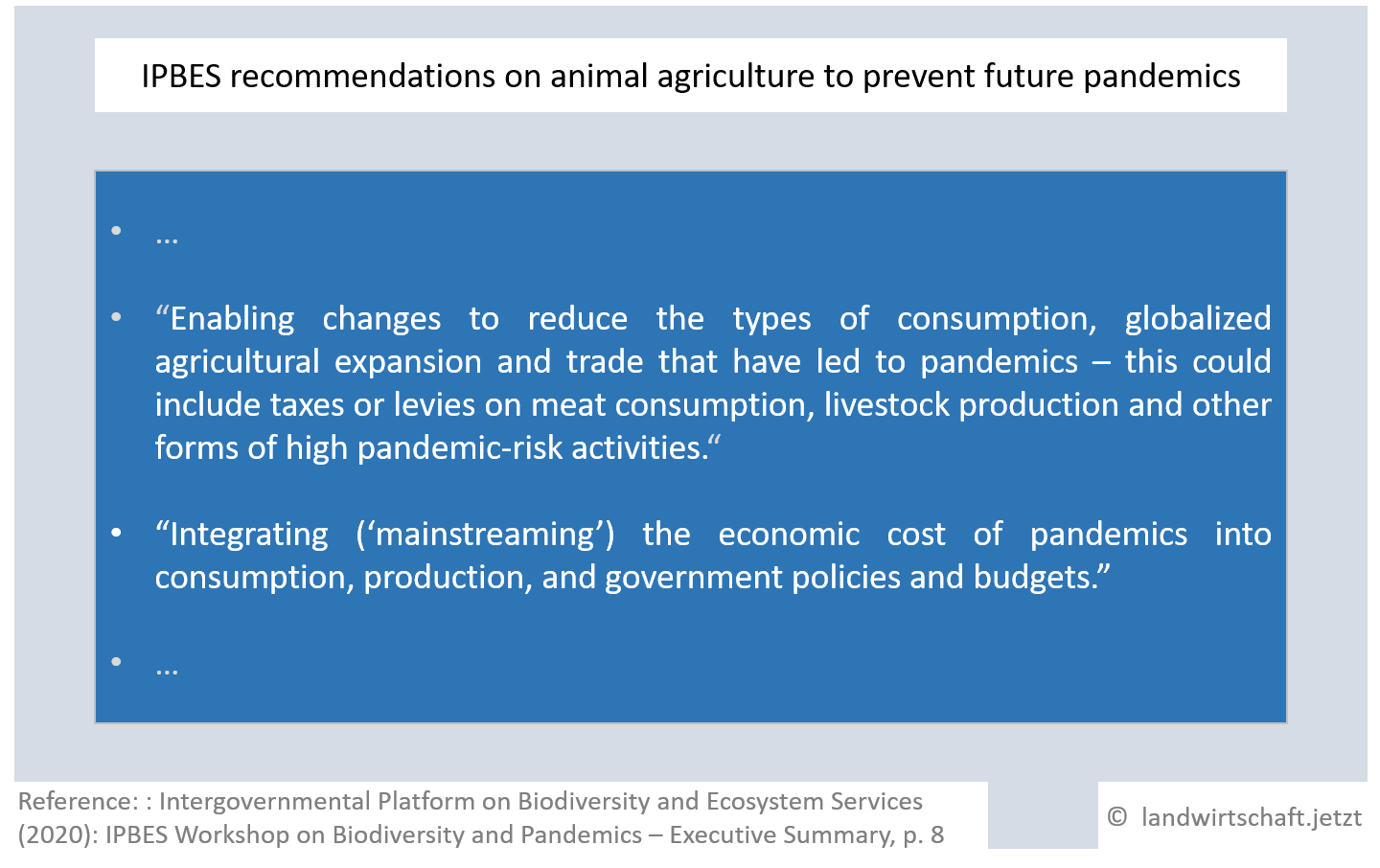
The World Biodiversity Council IPBES has therefore identified meat consumption and animal husbandry, among other things, as pandemic high-risk activities and proposes corresponding taxes and levies. The Council also calls for the economic costs of pandemics to be factored into consumption and production and for budgets for transformation processes to be made available in government budgets ([39], S.8).